If NVMe is the answer, what are the questions?
If NVMe is the answer, then what are the various questions that should be asked?
Some common questions that NVMe is the answer to include what is the difference between NVM and NVMe?
Is NVMe only for servers, does NVMe require fabrics and what benefit is NVMe beyond more IOPs.
Lets take a look at some of these common NVMe conversations and other questions.
Main Features and Benefits of NVMe
Some of the main feature and benefits of NVMe among others include:
- Lower latency due to improve drivers and increased queues (and queue sizes)
- Lower CPU used to handle larger number of I/Os (more CPU available for useful work)
- Higher I/O activity rates (IOPS) to boost productivity unlock value of fast flash and NVM
- Bandwidth improvements leveraging various fast PCIe interface and available lanes
- Dual-pathing of devices like what is available with dual-path SAS devices
- Unlock the value of more cores per processor socket and software threads (productivity)
- Various packaging options, deployment scenarios and configuration options
- Appears as a standard storage device on most operating systems
- Plug-play with in-box drivers on many popular operating systems and hypervisors
NVM and Media memory matters
Whats the differences between NVM and NVMe? Non-Volatile Memory (NVM) which as its name implies is persistent electronic memory medium where data is stored. Today you commonly know about NVMs as NAND flash Solid State Devices (SSD), along with NVRAM among others emerging storage class memories (SCM).
Emerging SCM such as 3D XPoint among other mediums (or media if you prefer) have the premises of boosting both read and write performance beyond traditional NAND flash, closer to DRAM, while having durability also closer to DRAM. For now let’s set the media and mediums aside and get back to how they or will be accessed as well as used.
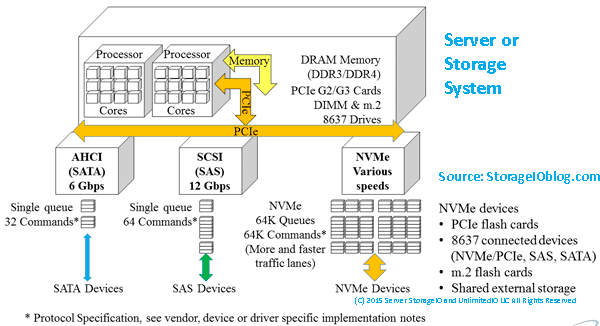
Server and Storage I/O Media access matters
NVM Express (e.g. NVMe) is a standard industry protocol for accessing NVM media (SSD and flash devices, storage system, appliances). If NVMe is the answer, then depending on your point of view, NVMe can be (or is) a replacement (today or in the future) for AHCI/SATA, Serial Attached SCSI (SAS). What this means is that NVMe can coexist or replace other block SCSI protocol implementations (e.g. Fibre Channel FCP aka FCP, iSCSI, SRP) as well as NBD (among others).
Similar to the SCSI command set that is implemented on different networks (e.g. iSCSI (IP), FCP (Fibre Channel), SRP (InfiniBand), SAS) NVMe as a protocol is now implemented using PCIe with form factors of add-in cards (AiC), M.2 (e.g. gum sticks aka next-gen form factor or NGFF) as well as U.2 aka 8639 drive form factors. There are also the emerging NVMe over Fabrics variants including FC-NVMe (e.g. NVMe protocol over Fibre Channel) which is an alternative to SCSI_FCP (e.g. SCSI on Fibre Channel). An example of a PCIe AiC that I have include the Intel 750 400GB NVMe (among others). You should be able to find the Intel among other NVMe devices from your prefered vendor as well as different venues including Amazon.com.
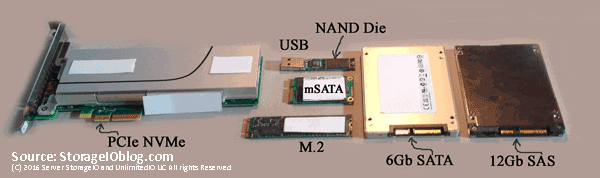
Left PCIe AiC x4 NVMe SSD, lower center M.2 NGFF, right SAS and SATA SSD
The following image shows an NVMe U.2 (e.g. 8639) drive form factor device that from a distance looks like a SAS device and connector. However looking closer some extra pins or connectors that present a PCIe Gen 3 x4 (4 PCIe lanes) connection from the server or enclosure backplane to the devices. These U.2 devices plug into 8639 slots (right) that look like a SAS slot that can also accommodate SATA. Remember, SATA can plug into SAS, however not the other way around.


Left NVMe U.2 drive showing PCIe x4 connectors, right, NVMe U.2 8639 connector
What NVMe U.2 means is that the 8639 slots can be used for 12Gbps SAS, 6Gbps SATA or x4 PCIe-based NVMe. Those devices in turn attach to their respective controllers (or adapters) and device driver software protocol stack. Several servers have U.2 or 8639 drive slots either in 2.5” or 1.8” form factors, sometimes these are also called or known as “blue” drives (or slots). The color coding simply helps to keep track of what slots can be used for different things.
Navigating your various NVMe options
If NVMe is the answer, then some device and component options are as follows.
NVMe device components and options include:
- Enclosures and connector port slots
- Adapters and controllers
- U.2, PCIe AIC and M.2 devices
- Shared storage system or appliances
- PCIe and NVMe switches
If NVMe is the answer, what to use when, where and why?
Why use an U.2 or 8639 slot when you could use PCIe AiC? Simple, your server or storage system may be PCIe slot constrained, yet have more available U.2 slots. There are U.2 drives from various vendors including Intel and Micro, as well as servers from Dell, Intel and Lenovo among many others.
Why and when would you use an NVMe M.2 device? As a local read/write cache, or perhaps a boot and system device on servers or appliances that have M.2 slots. Many servers and smaller workstations including Intel NUC support M.2. Likewise, there are M.2 devices from many different vendors including Micron, Samsung among others.
Where and why would you use NVMe PCIe AiC? Whenever you can and if you have enough PCIe slots of the proper form factor, mechanical and electrical (e.g. x1, x4, x8, x16) to support a particular card.
Can you mix and match different types of NVMe devices on the same server or appliance? As long as the physical server and its software (BIOS/UEFI, operating system, hypervisors, drivers) support it yes. Most server and appliance vendors support PCIe NVMe AiCs, however, pay attention to if they are x4, x8 both mechanical as well as electrical. Also, verify operating system and hypervisor device driver support. PCIe NVMe AiCs are available from Dell, Intel, Micron and many other vendors.
Networking with your Server and NVMe Storage
Keep in mind that context is important when discussing NVMe as there are devices for attaching as the back-end to servers, storage systems or appliances, as well as for front-end attachment (e.g. for attaching storage systems to servers). NVMe devices can also be internal to a server or storage system and appliance, or, accessible over a network. Think of NVMe as an upper-level command set protocol like SCSI that gets implemented on different networks (e.g. iSCSI, FCP, SRP).
How can NVMe use PCIe as a transport to use devices that are outside of a server? Different vendors have PCIe adapter cards that support longer distances (few meters) to attach to devices. For example, Dell EMC DSSD has a special dual port (two x4 ports) that are PCIe x8 cards for attachment to the DSSD shared SSD devices.
Note that there are also PCIe switches similar to SAS and InfiniBand among other switches. However just because these are switches, does not mean they are your regular off the shelf network type switch that your networking folks will know what to do with (or want to manage).
The following example shows a shared storage system or appliance being accessed by servers using traditional block, NAS file or object protocols. In this example, the storage system or appliance has implemented NVMe devices (PCIe AiC, M.2, U.2) as part of their back-end storage. The back-end storage might be all NVMe, or a mix of NVMe, SAS or SATA SSD and perhaps some high-capacity HDD.
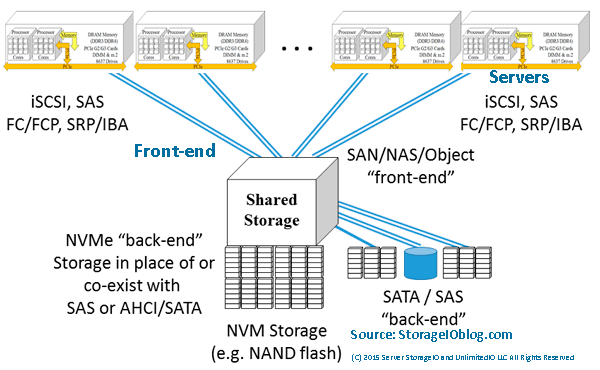
Servers accessing shared storage with NVMe back-end devices
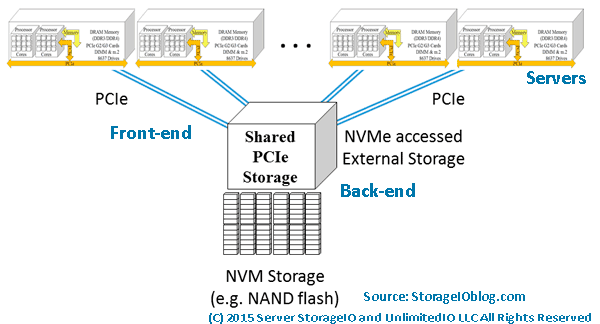
NVMe PCIe attached (via front-end) storage with various back-end devices
In addition to shared PCIe-attached storage such as Dell EMC DSSD similar to what is shown above, there are also other NVMe options. For example, there are industry initiatives to support the NVMe protocol to use shared storage over fabric networks. There are different fabric networks, they range from RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) based as well as Fibre Channel NVME (e.g. FC-NVME) among others.
An option that on the surface may not seem like a natural fit or leverage NVMe to its fullest is simply adding NVMe devices as back-end media to existing arrays and appliances. For example, adding NVMe devices as the back-end to iSCSI, SAS, FC, FCoE or other block-based, NAS file or object systems.
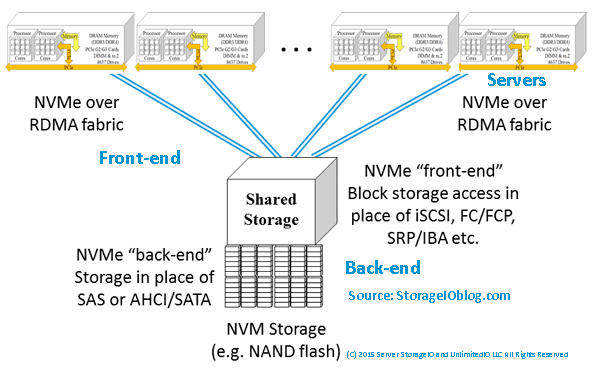
NVMe over a fabric network (via front-end) with various back-end devices
A common argument against using legacy storage access of shared NVMe is along the lines of why would you want to put a slow network or controller in front of a fast NVM device? You might not want to do that, or your vendor may tell you many reasons why you don’t want to do it particularly if they do not support it. On the other hand, just like other fast NVM SSD storage on shared systems, it may not be all about 100% full performance. Rather, for some environments, it might be about maximizing connectivity over many interfaces to faster NVM devices for several servers.
NVMe and server storage I/O performance
Is NVMe all about boosting the number of IOPS? NVMe can increase the number of IOPS, as well as support more bandwidth. However, it also reduces response time latency as would be expected with an SSD or NVM type of solution. The following image shows an example of not surprisingly an NVMe PCIe AiC x4 SSD outperforming (more IOPs, lower response time) compared to a 6Gb SATA SSD (apples to oranges). Also keep in mind that best benchmark or workload tool is your own application as well as your performance mileage will vary.
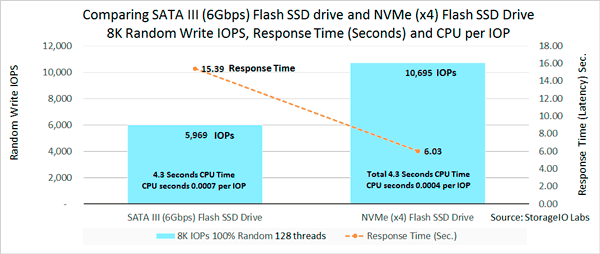
SATA SSD vs. NVMe PCIe AiC SSD IOPS, Latency and CPU per IOP
The above image shows the lower amount of CPU per IOP given the newer, more streamlined driver and I/O software protocol of NVMe. With NVMe there is less overhead due to the new design, more queues and ability to unlock value not only in SSD also in servers with more sockets, cores and threads.
What this means is that NVMe and SSD can boost performance for activity (TPS, IOPs, gets, puts, reads, writes). NVMe can also lower response time latency while also enabling higher throughput bandwidth. In other words, you get more work out of your servers CPU (and memory). Granted SSDs have been used for decades to boost server performance and in many cases, delay an upgrade to a newer faster system by getting more work out of them (e.g. SSD marketing 202).
NVMe maximizing your software license investments
What may not be so obvious (e.g. SSD marketing 404) is that by getting more work activity done in a given amount of time, you can also stretch your software licenses further. What this means is that you can get more out of your IBM, Microsoft, Oracle, SAP, VMware and other software licenses by increasing their effective productivity. You might already be using virtualization to increase server hardware efficiency and utilization to cut costs. Why not go further and boost productivity to increase your software license (as well as servers) effectiveness by using NVMe and SSDs?
Note that fast applications need fast software, servers, drivers, I/O protocols and devices.
Also just because you have NVMe present or PCIe does not mean full performance, similar to how some vendors put SSDs behind their slow controllers and saw, well slow performance. On the other hand vendors who had or have fast controllers (software, firmware, hardware) that were HDD or are even SSD performance constrained can see a performance boost.
Additional NVMe and related tips
If you have a Windows server and have not overridden, check your power plan to make sure it is not improperly set to balanced instead of high performance. For example using PowerShell issue the following command:
PowerCfg -SetActive “381b4222-f694-41f0-9685-ff5bb260df2e”
Another Windows related tip if you have not done so is enable task manager disk stats by issuing from a command line “diskperf –y”. Then display task manager and performance and see drive performance.
Need to benchmark, validate, compare or test an NVMe, SSD (or even HDD) device or system, there are various tools and workloads for different scenarios. Likewise those various tools can be configured for different activity to reflect your needs (and application workloads). For example, Microsoft Diskspd, fio.exe, iometer and vdbench sample scripts are shown here (along with results) as a starting point for comparison or validation testing.
Does M.2. mean you have NVMe? That depends as some systems implement M.2 with SATA, while others support NVMe, read the fine print or ask for clarification.
Do all NVMe using PCIe run at the same speed? Not necessarily as some might be PCIe x1 or x4 or x8. Likewise some NVMe PCIe cards might be x8 (mechanical and electrical) yet split out into a pair of x4 ports. Also keep in mind that similar to a dual port HDD, NVMe U.2 drives can have two paths to a server, storage system controller or adapter, however both might not be active at the same time. You might also have a fast NVMe device attached to a slow server or storage system or adapter.
Who to watch and keep an eye on in the NVMe ecosystem? Besides those mentioned above, others to keep an eye on include Broadcom, E8, Enmotus Fuzedrive (micro-tiering software), Excelero, Magnotics, Mellanox, Microsemi (e.g. PMC Sierra), Microsoft (Windows Server 2016 S2D + ReFS + Storage Tiering), NVM Express trade group, Seagate, VMware (Virtual NVMe driver part of vSphere ESXi in addition to previous driver support) and WD/Sandisk among many others.
Where To Learn More
Additional related content can be found at:
Additional learning experiences along with common questions (and answers), as well as tips can be found in Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials book.

What This All Means
NVMe is in your future, that was the answer, however there are the when, where, how, with what among other questions to be addressed. One of the great things IMHO about NVMe is that you can have it your way, where and when you need it, as a replacement or companion to what you have. Granted that will vary based on your preferred vendors as well as what they support today or in the future.
If NVMe is the answer, Ask your vendor when they will support NVMe as a back-end for their storage systems, as well as a front-end. Also decide when will your servers (hardware, operating systems hypervisors) support NVMe and in what variation. Learn more why NVMe is the answer and related topics at www.thenvmeplace.com
Ok, nuff said, for now.
Gs
Greg Schulz – Microsoft MVP Cloud and Data Center Management, VMware vExpert 2010-2017 (vSAN and vCloud). Author of Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials (CRC Press), as well as Cloud and Virtual Data Storage Networking (CRC Press), The Green and Virtual Data Center (CRC Press), Resilient Storage Networks (Elsevier) and twitter @storageio. Courteous comments are welcome for consideration. First published on https://storageioblog.com any reproduction in whole, in part, with changes to content, without source attribution under title or without permission is forbidden.
All Comments, (C) and (TM) belong to their owners/posters, Other content (C) Copyright 2006-2026 Server StorageIO and UnlimitedIO. All Rights Reserved. StorageIO is a registered Trade Mark (TM) of Server StorageIO.

