2018 Hot Popular New Trending Data Infrastructure Vendors to Watch

2018 Hot Popular New Trending Data Infrastructure Vendors to Watch
Here is the 2018 Hot Popular New Trending Data Infrastructure Vendors To Watch which includes startups as well as established vendors doing new things. This piece follows last year’s hot favorite trending data infrastructure vendors to watch list (here), as well as who will be top of storage world in a decade piece here.
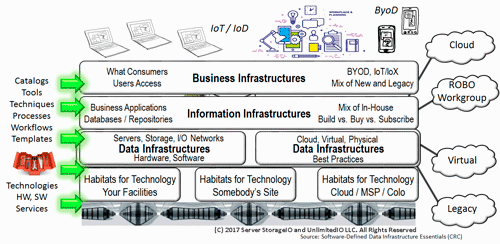
Data Infrastructures Support Information Systems Applications and Their Data
Data Infrastructures are what exists inside physical data centers and cloud availability zones (AZ) that are defined to provide traditional, as well as cloud services. Cloud and legacy data infrastructures are combined by hardware (server, storage, I/O network), software along with management tools, policies, tradecraft techniques (skills), best practices to support applications and their data. There are different types of data infrastructures to meet the needs of various environments that range in size, scope, focus, application workloads, along with Performance and capacity.
Another important aspect of data infrastructures is that they exist to protect, preserve, secure and serve applications that transform data into information. This means that availability and Data Protection including archive, backup, business continuance (BC), business resiliency (BR), disaster recovery (DR), privacy and security among other related topics, technology, techniques, and trends are essential data infrastructure topics.
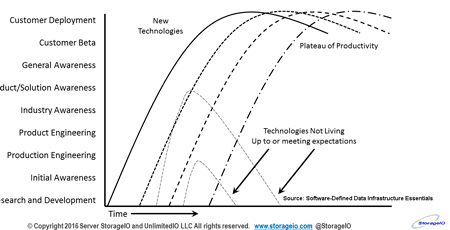
Different timelines of adoption and deployment for various audiences
2018 Hot Popular New Trending Data Infrastructure Vendors to Watch
Some of those on this year’s list are focused on different technology areas, while others on size or types of vendors, suppliers, service providers. Others on the list are focused on who is new, startup, evolving, or established which varies from if you are an industry insider or IT customer environment. Meanwhile others new and some are established doing new things, mix of some you may not have heard of for those who want or need to have the most current list to rattle off startups for industry adoption (and deployment), as well as what some established players are doing that might lead to customer deployment (and adoption).
AMD – The AMD EPYC family of processors is opening up new opportunities for AMD to challenge Intel among others for a more significant share of the general-purpose compute market in support of data center and data infrastructure markets. An advantage that AMD has and is playing to in the industry speeds feeds, slots and watts price performance game is the ability to support more memory and PCIe lanes per socket than others including Intel. Keep in mind that PCIe lanes will become even more critical as NVMe deployment increases, as well as the use of GPU’s and faster Ethernet among other devices. Name brand vendors including Dell and HPE among others have announced or are shipping AMD EPYC based processors.
Aperion – Cloud and managed service provider with diverse capabilities.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) – Continues to expand its footprint regarding regions, availability zones (AZ) also known as data centers in regions, as well as some services along with the breadth of those capabilities. AWS has recently announced a new Snowball Edge (SBE) which in the past has been a data migration appliance now enhanced with on-prem Elastic Cloud Compute (EC2) capabilities. What this means is that AWS can put on-prem compute capabilities as part of a storage appliance for short-term data movement, migration, conversion, importing of virtual machines and other items.
On the other hand, AWS can also be seen as using SBE as a first entry to placing equipment on-prem for hybrid clouds, or, converged infrastructure (CI), hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI), cloud in a box similar to Microsoft Azure Stack, as well as CI/HCI solutions from others.
My prediction near term, however, is that CI/HCI vendors will either ignore SBE, downplay it, create some new marketing on why it is not CI/HCI or fud about vendor lock-in. In other words, make some popcorn and sit back, watch the show.
Backblaze – Low-cost, high-capacity cloud storage for backup and archiving provider known for their quarterly disk drive reliability ratings (or failure) reports. They have been around for a while, have a good reputation among those who use their services for being a low-cost alternative to the larger providers.
Barefoot networks – Some of you may already be aware of or following Barefoot Networks, while others may not have heard of them outside of the networking space. They have some impressive capabilities, are new, you probably have not heard of them, thus an excellent addition to this list.
Cloudian – Continue to evolve and no longer just another object storage solution, Cloudian has been expanding via organic technology development, as well as acquisitions giving them a broad portfolio of software-defined storage and tiering from on-prem to the cloud, block, file and object access.
Cloudflare – Not exactly a startup, some of you may know or are using Cloudflare, while to others, their role as a web cache, DNS, and other service is transparent. I have been using Cloudflare on my various sites for over a year, and like the security, DNS, cache and analytics tools they provide as a customer.
Cobalt Iron – For some, they might be new, Software-defined Data protection and management is the name of the game over at Cobalt Iron which has been around a few years under the radar compared to more popular players. If you have or are involved with IBM Tivoli aka TSM based backup and data protection among others, check out the exciting capabilities that Cobalt can bring to the table.
CTERA – Having been around for a while, to some they might not be a startup, on the other hand, they may be new to others while offering new data and file management options to others.
DataCore – You might know of DataCore for their software-defined storage and past storage hypervisor activity. However, they have a new piece of software MaxParallel that boost server storage I/O performance. The software installs on your Windows Server instance (bare metal, VM, or cloud instance) and shows you performance with and without acceleration which you can dynamically turn off and off.
DataDirect Networks (DDN) – Recently acquired Lustre assets from Intel, now picking up the storage startup Tintri pieces after it ceased operations. What this means is that while beefing up their traditional High-Performance Compute (HPC) and Super Compute (SC) focus, DDN is also expanding into broader markets.
Dell Technologies – At its recent Dell Technology World event in Las Vegas during late April, early May 2018, several announcements were made, including some tied to emerging Gen-Z along with composability. More recently, Dell Technologies along with VMware announced business structure and finance changes. Changes include VMware declaring a dividend, Dell Technologies being its largest shareholder will use proceeds to fund restricting and debt service. Read more about VMware and Dell Technology business and financial changes here.
Densify – With a name like Densify no surprise they propose to drive densification and automation with AI-powered deep learning to optimize application resource use across on-prem software-defined virtual as well as cloud instances and containers.
FlureDB – If you are into databases (SQL or NoSQL), as well as Blockchain or distributed ledgers, check out FlureDB.
Innovium.com – When it comes to data infrastructure and data center networking, Innovium is probably not on your radar, however, keep an eye on these folks and their TERALYNX switching silicon to see where it ends up given their performance claims.
Komprise – File, and data management solutions including tiering along with partners such as IBM.
Kubernetes – A few years ago OpenStack, then Docker containers was the favorite and trending discussion topic, then Mesos and along comes Kubernetes. It’s safe to say, at least for now, Kubernetes is settling in as a preferred open source industry and customer defecto choice (I want to say standard, however, will hold off on that for now) for container and related orchestration management. Besides, do it yourself (DiY) leveraging open source, there are also managed AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), Azure Kubernetes Services (AKS), Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), and VMware Pivotal Container Service (PKS) among others. Besides Azure, Microsoft also includes Kubernetes support (along with Docker and Windows containers) as part of Windows Servers.
ManageEngine (part of Zoho) – Has data infrastructure monitoring technology called OpManager for keeping an eye on networking.
Marvel – Marvel may not be a familiar name (don’t confuse with comics), however, has been a critical component supplier to partners whose server or storage technology you may be familiar with or have yourself. Server, Storage, I/O Networking chip maker has closed on its acquisition of Cavium (who previously bought Qlogic among others). The combined company is well positioned as a key data infrastructure component supplier to various partners spanning servers, storage, I/O networking including Fibre Channel (FC), Ethernet, InfiniBand, NVMe (and NVMeoF) among others.
Mellanox – Known for their InfiniBand adapters, switches, and associated software, along with growing presence in RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE), they are also well positioned for NVMe over Fabrics among other growth opportunities following recent boardroom updates, along with technology roadmap’s.
Microsoft – Azure public cloud continues to evolve similarly to AWS with more region locations, availability zone (AZ) data centers, as well as features and extensions. Microsoft also introduced about a year ago its hybrid on-prem CI/HCI cloud in a box platform appliance Azure Stack (read about my test drive here). However, there is more to Microsoft than just their current cloud first focus which means Windows (desktop), as well as Server, are also evolving. Currently, in public preview, Windows Server 2019 insiders build available to try out many new capabilities, some of which were covered in the recent free Microsoft Virtual Summit held in June. Key themes of Windows Server 2019 include security, performance, hybrid cloud, containers, software-defined storage and much more.
Microsemi – Has been around for a while is the combination of some vendors you may not have heard of or heard about in some time including PMC-Sierra (acquired Adaptec) and Vitesse among others. The reason I have Microsemi on this list is a combination of their acquisitions which might be an indicator of whom they pick up next. Another reason is that their components span data infrastructure topics from servers, storage, I/O and networking, PCIe and many more.
NVIDIA – GPU high performance compute and related compute offload technologies have been accessible for over a decade. More recently with new graphics and computational demands, GPU such as those NVIDIA are in need. Demand includes traditional graphics acceleration for physical and virtual, augmented and virtual reality, as well as cloud, along with compute-intensive analytics, AI, ML, DL along with other cognitive workloads.
NGDSystems (NGD) – Similar to what NVIDIA and other GPU vendors do for enabling compute offload for specific applications and workloads, NGD is working on a variation. That variation is to move offload compute capabilities for the server I/O storage-intensive workloads closer, in fact into storage system components such as SSDs and emerging SCMs and PMEMs. Unlike GPU based applications or workloads that tend to be more memory and compute intensive, NGD is positioned for applications that are the server I/O and storage intensive.
The premise of NGD is that they move the compute and application closer to where the data is, eliminating extra I/O, as well as reducing the amount of main server memory and compute cycles. If you are familiar with other server storage I/O offload engines and systems such as Oracle Exadata database appliance NGD is working at a tighter integration granularity. How it works is your application gets ported to run on the NGD storage platform which is SSD based and having a general-purpose processor. Your application is initiated from a host server, where it then runs on the NGD meaning I/Os are kept local to the storage system. Keep in mind that the best I/O is the one that you do not have to do, the second best is the one with the least resource or user impact.
Opvisor – Performance activity and capacity monitoring tools including for VMware environments.
Pavillon – Startup with an interesting NVMe based hardware appliance.
Quest – Having gained their independence as a free-standing company since divestiture from Dell Technologies (Dell had previously acquired Quest before EMC acquisition), Quest continues to make their data infrastructure related management tools available. Besides now being a standalone company again, keep an eye on Quest to see how they evolve their existing data protection and data infrastructure resource management tools portfolio via growth, acquisition, or, perhaps Quest will be on somebody else’s future growth list.
Retrospect – Far from being a startup, after gaining their independence from when EMC bought them several years ago, they have since continued to enhance their data protection technology. Disclosure, I have been a Retrospect customer since 2001 using it for on-site, as well as cloud data protection backups to the cloud.
Rubrik – Becoming more of a data infrastructure household name given their expanding technology portfolio and marketing efforts. More commonly known in smaller customer environments, as well as broadly within industry insider circles, Rubrik has potential with continued technology evolution to move further upmarket similar to how Commvault did back in the late 90s, just saying.
SkyScale – Cloud service provider that offers dedicated bare metal, as well as private, hybrid cloud instances along with GPU to support AI, ML, DL and other high performance, compute workloads.
Snowflake – The name does not describe well what they do or who they are. However, they have an interesting cloud data warehouse (old school) large-scale data lakes (new school) technologies.
Strongbox – Not to be confused with technology such as those from Iosafe (e.g., waterproof, fireproof), Strongbox is a data protection storage solution for storing archives, backups, BC/BR/DR data, as well as cloud tiering. For those who are into buzzword bingo, think cloud tiering, object, cold storage among others. The technology evolved out of Crossroads and with David Cerf at the helm has branched out into a private company with keeping an eye on.
Storbyte – With longtime industry insider sales and marketing pro-Diamond Lauffin (formerly Nexsan) involved as Chief Evangelist, this is worth keeping an eye on and could be entertaining as well as exciting. In some ways it could be seen as a bit of Nexsan meets NVme meets NAND Flash meets cost-effective value storage dejavu play.
Talon – Enterprise storage and management solutions for file sharing across organizations, ROBO and cloud environments.
Ubitqui – Also known as UBNT is a data infrastructure networking vendor whose technologies span from WiFi access points (AP), high-performance antennas, routing, switching and related hardware, along with software solutions. UBNT is not as well-known in more larger environments as a Cisco or others. However, they are making a name for themselves moving from the edge to the core. That is, working from the edge with AP and routers, firewalls, gateways for the SMB, ROBO, SOHO as well as consumer (I have several of their APs, switches, routers and high-performance antennas along with management software), these technologies are also finding their way into larger environments.
My first use of UBNT was several years ago when I needed to get an IP network connection to a remote building separated by several hundred yards of forest. The solution I found was to get a pair of UBNT NANO Apps, put them in secure bridge mode; now I have a high-performance WiFi service through a forest of trees. Since then have replaced an older Cisco router, several Cisco, and other APs, as well as the phased migration of switches.
UpdraftPlus– If you have a WordPress web or blog site, you should also have a UpdraftPlus plugin (go premium btw) for data protection. I have been using Updraft for several years on my various sites to backup and protect the MySQL databases and all other content. For those of you who are familiar with Spanning (e.g., was acquired by EMC then divested by Dell) and what they do for cloud applications, UpdraftPlus does similar for lower-end, smaller cloud-based applications.
Vexata – Startup scale out NVMe storage solution.
VMware – Expanding their cloud foundation from on-prem to in and on clouds including AWS among others. Data Infrastructure focus continues to expand from core to edge, server, storage, I/O, networking. With recent Dell Technologies and VMware declaring a dividend, should be interesting to see what lies ahead for both entities.
What About Those Not Mentioned?
By the way, if you were wondering about or why others are not in the above list, simple, check out last year’s list which includes Apcera, Blue Medora, Broadcom, Chelsio, Commvault, Compuverde, Datadog, Datrium, Docker, E8 Storage, Elastifile, Enmotus, Everspin, Excelero, Hedvig, Huawei, Intel, Kubernetes, Liqid, Maxta, Micron, Minio, NetApp, Neuvector, Noobaa, NVIDA, Pivot3, Pluribus Networks, Portwork, Rozo Systems, ScaleMP, Storpool, Stratoscale, SUSE Technology, Tidalscale, Turbonomic, Ubuntu, Veeam, Virtuozzo and WekaIO. Note that many of the above have expanded their capabilities in the past year and remain, or have become even more interesting to watch, while some might be on the future where are they now list sometime down the road. View additional vendors and service providers via our industry links and resources page here.
What About New, Emerging, Trending and Trendy Technologies
Bitcoin and Blockchain storage startups, some of which claim or would like to replace cloud storage taking on giants such as AWS S3 in the not so distant future have been popping up lately. Some of these have good and exciting stories if they can deliver on the hype along with the premise. A couple of names to drop include among others Filecoin, Maidsafe, Sia, Storj along with services from AWS, Azure, Google and a long list of others.
Besides Blockchain distributed ledgers, other technologies and trends to keep an eye on include compute processes from ARM to SoC, GPU, FPGA, ASIC for offload and specialized processing. GPU, ASIC, and FPGA are appearing in new deployments across cloud providers as they look to offload processing from their general servers to derive total effective productivity out of them. In other words, innovating by offloading to boost their effective return on investment (old ROI), as well as increase their return on innovation (the new ROI).
Other data infrastructure server I/O which also ties into storage and network trends to watch include Gen-Z that some may claim as the successor to PCIe, Ethernet, InfiniBand among others (hint, get ready for a new round of “something is dead” hype). Near-term the objective of Gen-Z is to coexist, complement PCIe, Ethernet, CPU to memory interconnect, while enabling more granular allocation of data infrastructure resources (e.g., composability). Besides watching who is part of the Gen-Z movement, keep an eye on who is not part of it yet, specifically Intel.
NVMe and its many variations from a server internal to networked NVMe over Fabrics (NVMeoF) along with its derivatives continue to gain both industry adoption, as well as customer deployment. There are some early NVMeoF based server storage deployments (along with marketing dollars). However, the server side NVMe customer adoption is where the dollars are moving to the vendors. In other words, it’s still early in the bigger broader NVMe and NVMeoF game.
Where to learn more
Learn more about data infrastructures and related topics via the following links:
Additional learning experiences along with common questions (and answers), as well as tips can be found in Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials book.

What this all means
Let’s see how those mentioned last year as well as this year, along with some new and emerging vendors, service providers who did not get said end up next year, as well as the years after that.

Different timelines of adoption and deployment for various audiences
Keep in mind that there is a difference between industry adoption and customer deployment, granted they are related. Likewise let’s see who will be at the top in three, five and ten years, which means some of the current top or favorite vendors may or may not be on the list, same with some of the established vendors. Meanwhile, check out the 2018 Hot Popular New Trending Data Infrastructure Vendors to Watch.
Ok, nuff said, for now.
Cheers Gs
Greg Schulz – Microsoft MVP Cloud and Data Center Management, VMware vExpert 2010-2018. Author of Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials (CRC Press), as well as Cloud and Virtual Data Storage Networking (CRC Press), The Green and Virtual Data Center (CRC Press), Resilient Storage Networks (Elsevier) and twitter @storageio. Courteous comments are welcome for consideration. First published on https://storageioblog.com any reproduction in whole, in part, with changes to content, without source attribution under title or without permission is forbidden.
All Comments, (C) and (TM) belong to their owners/posters, Other content (C) Copyright 2006-2026 Server StorageIO and UnlimitedIO. All Rights Reserved. StorageIO is a registered Trade Mark (TM) of Server StorageIO.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

