Access Availability RAID Erasure Codes including LRC Deep Dive
Companion to Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials – Cloud, Converged, Virtual Fundamental Server Storage I/O Tradecraft ( CRC Press 2017)

By Greg Schulz – www.storageioblog.com November 26, 2017
This is Part 3 of a multi-part series on Data Protection fundamental tools topics techniques terms technologies trends tradecraft tips as a follow-up to my Data Protection Diaries series, as well as a companion to my new book Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials – Cloud, Converged, Virtual Server Storage I/O Fundamental tradecraft (CRC Press 2017).

Click here to view the previous post Part 2 Reliability, Availability, Serviceability (RAS) Data Protection Fundamentals, and click here to view the next post Part 4 Data Protection Recovery Points (Archive, Backup, Snapshots, Versions).
Post in the series includes excerpts from Software Defined Data Infrastructure (SDDI) pertaining to data protection for legacy along with software defined data centers ( SDDC), data infrastructures in general along with related topics. In addition to excerpts, the posts also contain links to articles, tips, posts, videos, webinars, events and other companion material. Note that figure numbers in this series are those from the SDDI book and not in the order that they appear in the posts.
In this post part of the Data Protection diaries series as well as companion to Chapter 9 of SDDI Essentials book, we are going on a longer, deeper dive. We are going to look at availability, access and durability including mirror, replication, RAID including various traditional and newer parity approaches such as Erasure Codes ( EC), Local Reconstruction Code (LRC), Reed Solomon (RS) also known as RAID 2 among others. Later posts in this series look at point in time data protection to support recovery to a given time (e.g. RPO), while this and the previous post look at maintaining access and availability.
Keep in mind that if something can fail, it probably will, also that everything is not the same meaning different environments, application workloads (along with their data). Different environments and applications have diverse performance, availability, capacity economic (PACE) attributes, along with service level objectives ( SLOs). Various SLOs include PACE attributes, recovery point objectives ( RPO), recovery time objective ( RTO) among others.
Availability, accessibility and durability (see part two in this series) along with associated RAS topics are part of what enable RTO, as well as meet Faults (or failures) to tolerate ( FTT). This means that different fault tolerance modes ( FTM) determine what technologies, tools, trends and techniques to use to meet different RTO, FTT and application PACE needs.
Maintaining access and availability along with durability (e.g. how many copies of data as well as where stored) protects against loss or failure of a component device ( SSD, HDDs, adapters, power supply, controller), node or system, appliance, server, rack, clusters, stamps, data center, availability zones, regions, or other Fault or Failure domains spanning hardware, software, and services.
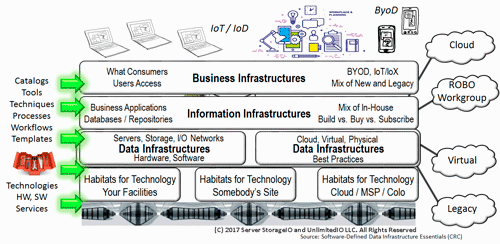
Figure 1.5 Data Infrastructures and other IT Infrastructure Layers
Data Protection Access Availability RAID Erasure Codes
This is a good place to mention some context for RAID and RAID array, which can mean different things pertaining to Data Protection. Some people associate RAID with a hardware storage array, or with a RAID card. Other people consider an array to be a storage array that is a RAID enabled storage system. A trend is to refer to legacy storage systems as RAID arrays or hardware-based RAID, to differentiate from newer implementations.
Context comes into play in that a RAID group (i.e., a collection of HDDs or SSD that is part of a RAID set) can be referred to as an array, a RAID array, or a virtual array. What this means is that while some RAID implementations may not be relevant, there are many new and evolving variations extending parity based protection making at least software-defined RAID still relevant
Keep context in mind, and don’t be afraid to ask what someone is referring to: a particular vendor storage system, a RAID implementation or packaging, a storage array, or a virtual array. Also keep the context of the virtual array in perspective vs. storage virtualization and virtual storage. RAID as a term is used to refer to different modes such as mirroring or parity, and parity can be legacy RAID 4, 5, or 6 along with erasure codes (EC). Note some people refer to erasure codes in the context of not being a RAID system, which can be an inference to not being a legacy storage system running hardware RAID (e.g. not software or software defined).
The following figure (9.13) shows various availability protection schemes (e.g. not recovery point) that maintain access while protecting against loss of a component, device, system, server, site, region or other part of a fault domain. Since everything is not the same with environments and applications having different Performance Availability Capacity Economic ( PACE) attributes, there are various approaches for enabling availability along with accessibility.
Keep in mind that RAID and Erasure codes along with their various, as well as replication and mirroring by themselves are not a replacement for backup or other point in time (e.g. enable recovery point) protection.
Instead, availability technologies such as RAID and erasure code along with mirror as well as replication need to be combined with snapshots, point in time copies, consistency points, checkpoints, backups among other recovery point protection for complete data protection.
Speaking of replacement for backup, while many vendors and their pundits claIm or want to see backup as being dead, as long as they keep talking about backup instead of broader data protection backup will remain alive.
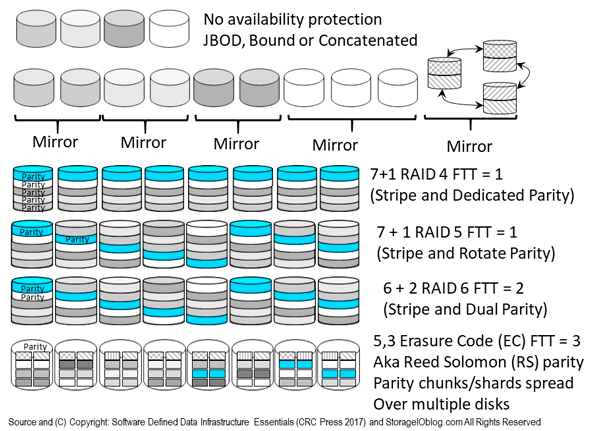
Figure 9.13 Various RAID, Mirror, Parity and Erasure Code (EC) approaches
Different RAID levels (including parity, EC, LRC and RS based) will affect storage energy effectiveness, similar to various SSD or HDD performance capacity characteristics; however, a balance of performance, availability, capacity, and energy needs to occur to meet application service needs. For example, RAID 1 mirroring or RAID 10 mirroring and striping use more HDDs and, thus, power, but will yield better performance than RAID 6 and erasure code parity protection.
| Normal performance | Availability | Performance overhead | Rebuild overhead | Availability overhead |
RAID 0 (stripe) | Very good read & write | None | None | Full volume restore | None |
RAID 1 (mirror or replicate) | Good reads; writes = device speed | Very good; two or more copies | Multiple copies can benefit reads | Re-synchronize with existing volume | 2:1 for dual, 3:1 for three-way copies |
RAID 4 (stripe with dedicated parity, i.e., 4 + 1 = 5 drives total) | Poor writes without cache | Good for smaller drive groups and devices | High on write without cache (i.e., parity) | Moderate to high, based on number and type of drives | Varies; 1 Parity/N, where N = number of devices |
RAID 5
(stripe with rotating parity, 4 + 1 = 5 drives) | Poor writes without cache | Good for smaller drive groups and devices | High on write without cache (i.e., parity) | Moderate to high, based on number and type of drives | Varies
1 Parity/N, where N = number of devices |
RAID 6
(stripe with dual parity, 4 + 2 = 6 drives) | Poor writes without cache | Better for larger drive groups and devices | High on write without cache (i.e., parity) | Moderate to high, based on number and type of drives | Varies; 2 Parity/N, where N = number of devices |
RAID 10
(mirror and stripe) | Good | Good | Minimum | Re-synchronize with existing volume | Twice mirror capacity stripe drives |
Reed-Solomon (RS) parity, also known as erasure code (EC), local reconstruction code (LRC), and SHEC | Ok for reads, slow writes; good for static and cold data with front-end cache | Good | High on writes (CPU for parity calculation, extra I/O operations) | Moderate to high, based on number and type of drives, how implemented, extra I/Os for reconstruction | Varies, low overhead when using large number of devices; CPU, I/O, and network overhead. |
Table 9.3 Common RAID Characteristics
Besides those shown in table 9.3, other RAID including parity based approaches include 2 (Reed Solomon), 3 (synchronized stripe and dedicated parity) along with others including combinations such as 10, 01, 50, 60 among others.
Similar to legacy parity-based RAID, some erasure code implementations use narrow drive groups while others use larger ones to increase protection and reduce capacity overhead. For example, some larger enterprise-class storage systems (RAID arrays) use narrow 3 + 1 or 4 + 1 RAID 5 or 4 + 2 or 6 + 2 RAID 6, which have higher protection storage capacity overhead and fault=impact footprint.
On the other hand, many smaller mid-range and scale-out storage systems, appliances, and solutions support wide stripes such as 7 + 1, 15 + 1, or larger RAID 5, or 14 + 2 or larger RAID 6. These solutions trade the lower storage capacity protection overhead for risk of a multiple drive failures or impacts. Similarly, some EC implementations use relatively small groups such as 6, 2 (8 drives) or 4, 2 (6 drives), while others use 14, 4 (18 drives), 16, 4 (20 drives), or larger.
Table 9.4 shows options for a number of data devices (k) vs. a number of protect devices (m).
k
(data devices) | m
(protect devices) | Availability;
Resiliency | Space capacity overhead | Normal performance | FTT | Comments;
Examples |
Narrow | Wide | Very good;
Low impact of rebuild | Very high | Good (R/W) | Very good | Trade space for RAS;
Larger m vs. k;
1, 1; 1, 2; 2, 2; 4, 5 |
Narrow | Narrow | Good | Good | Good (R/W) | Good | Use with smaller drive groups;
2, 1; 3, 1; 6, 2 |
Wide | Narrow | Ok to good;
With larger m value | Low as m gets larger | Good (read);
Writes can be slow | Ok to good | Smaller m can impact rebuild;
3, 1; 7, 1; 14, 2; 13, 3 |
Wide | Wide | Very good;
Balanced | High | Good | Very good | Trade space for RAS;
2, 2; 4, 4; 8, 4; 18, 6 |
Table 9.4. Comparing Various Data Device vs. Protect Device Configurations
Note that wide k with no m, such as 4, 0, would not have protection. If you are focused on reducing costs and storage space capacity overhead, then a wider (i.e., more devices) with fewer protect devices might make sense. On the other hand, if performance, availability, and minimal to no impact during rebuild or reconstruction are important, then a narrower drive set, or a smaller ratio of data to protect drives, might make sense.
Also note that the higher or larger the RAID number, or parity scheme, or number of "m" devices in a parity and erasure code group may not be better, likewise smaller may not be better. What is better is which approach meets your specific application performance, availability, capacity, economic (PACE) needs, along with SLO, RTO, RPO requirements. What can also be good is to use hybrid approaches combining different technologies and tools to facilitate both access, availability, durability along with point in time recovery across different layers of granularity (e.g. device, drive, adapter, controller, cabinet, file system, data center, etc).
Some focus on the lower level RAID as the single or primary point of protection, however watch out for that being your single point of failure as well. For example, instead of building a resilient RAID 10 and then neglecting to have adequate higher level access, as well as recovery point protection, combine different techniques including file system protection, snapshots, and backups among others.
Figure 9.14 shows various options and considerations for balancing between too many or too few data (k) and protect (m) devices. The balance is about enabling particular FTT along with PACE attributes and SLO. This means, for some environments or applications, using different failure-tolerant modes ( FTM) in various combinations as well as configurations.
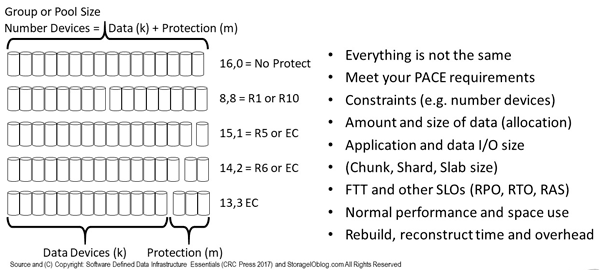
Figure 9.14 Comparing various data drive to protection devices
Figure 9.14 top shows no protection overhead (with no protection); the bottom shows 13 data drives and three protection drives in an EC (RS or LRC among others) configuration that could tolerate three devices failing before loss of data or access occurs. In between are various options that can also be scaled up or down across a different number of devices ( HDDs, SSD, or systems).
Some solutions allow the user or administrator to configure the I/O chunk, slabs, shard, or stripe size, for example, from 8 KB to 256 KB to 1 MB (or larger), aligning with application workload and I/O profiles. Other options include the ability to set or disable read-ahead, write-through vs. write-back cache (with battery-protected cache), among other options.
The width or number of devices in a RAID parity or erasure group is based on a combination of factor, including how much data is to be stored and what your FTT objective is, along with spreading out protection overhead. Another consideration is whether you have large or small files and objects.
For example, if you have many small files and a wide stripe, parity, or erasure code set with a large chunk or shard size, you may not have an optimal configuration from a performance perspective.
The following figure shows combing various data protection availability and accessibility technologies including local as well as remote mirroring and replication, along with parity or erasure code (including LRC, RS, SHEC among others) approaches. Instead of just using one technology, a hybrid approach is used leveraging mirror (local on SSD) and replication across sites including asynchronous and synchronous. Replication modes include Asynchronous (time-delayed, eventual consistency) for longer distance, higher latency networks, and synchronous (strong consistency, real-time) for short distance or low-latency networks.
Note that the mirror and replication can be done in software deployed as part of a storage system, appliance or as tin-wrapped software, virtual machine, virtual storage appliance, container or some other deployment mode. Likewise RAID, parity and erasure code software can be deployed and packaged in different ways.
In addition to mirror and replication, solutions are also using parity based including erasure code variations for lower cost, less active data. In other words, the mirror on SSD handles active hot data, as well as any buffering or cache, while lower performance, higher capacity, lower cost data gets de-staged or migrated to a parity erasure code tier. Some vendors, service provider and solutions leveraging variations of the approach in figure 9.15 include Microsoft ( Azure and Windows) and VMware among others.
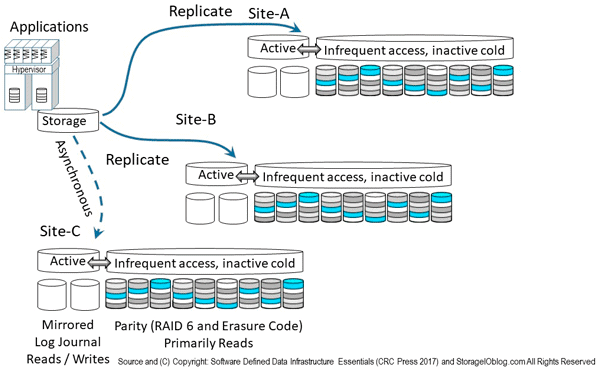
Figure 9.15 Combining various availability data protection techniques
A tradecraft skill is finding the balance, knowing your applications, the data, and how the data is allocated as well as used, then leveraging that insight and your experience to configure to meet your application PACE requirements.
Consider:
- Number of drives (width) in a group, along with protection copies or parity
- Balance rebuild performance impact and time vs. storage space overhead savings
- Ability to mix and match various devices in different drive groups in a system
- Management interface, tools, wizards, GUIs, CLIs, APIs, and plug-ins
- Different approaches for various applications and environments
- Context of a physical RAID array, system, appliance, or solution vs. logical
Erasure Codes (EC)
Erasure Codes ( EC) combines advanced protection with variable space capacity overhead over many drives, devices, or systems using large parity chunks, shards compared to traditional parity RAID approaches. There are many variations of EC as well as parity based approaches, some are tied to Reed Solomon (RS) codes while others use different approaches.
Note that some EC are optimized for reducing the overhead and cost of storing data (e.g. less space capacity) for inactive, or primarily read data. Likewise, some EC or variations are optimized for performance of reads/writes as well as reducing overhead of rebuild, reconstructions, repairs with least impact. Which EC or parity derivative approach is best depends on what you are trying to do or impact to avoid.
Reed Solomon (RS) codes
Reed Solomon (RS) codes are advanced parity protection mathematical algorithm technique that works well on large amounts of data providing protection with lower space capacity overhead depending on how configured. Many Erasure Codes (EC) are based on derivatives of RS. Btw, did you know (or remember) that RAID 2 (rarely used with few legacy implementations) has ties to RS codes? Here are some additional links to RS including via Backblaze, CMU, and Dr Dobbs.
Local Reconstruction Codes (LRC)
Microsoft leverages LRC in Azure as well as in Windows Servers. LRC are optimized for a balance of protection, space capacity savings, normal performance as well as reducing impact on running workloads during a repair, rebuild or reconstruction. One of the tradeoffs that LRC uses is to add some amount of additional space capacity in exchange for normal and abnormal (e.g. during repair) performance improvements. Where RS, EC and other parity based derivatives typically use a (k,m) nomenclature (e.g. data, protection), LRC adds an extra variable to help with constructions (k,m,n).
Some might argue that LRC are not as space efficient as other EC, RS or parity derivative variations of which the counter argument can be that some of those approaches are not as performance effective. In other words, everything is not the same, one approach does not or should not have to be applied to all, unless of course your preferred solution approach can only do one thing.
Additional LRC related material includes:
- (PDF by Microsoft) LRC Erasure Coding in Windows Storage Spaces
- (Microsoft Usenix Paper) Best Paper Award Erasure Coding in Azure
- (Via MSDN Shared) Azure Storage Erasure Coding with LRC
- (Via Microsoft) Azure Storage with Strong Consistency
- (Paper via Microsoft) 23rd ACM Symposium on Operating Systems Principles (SOSP)
- (Microsoft) Erasure Coding in Azure with LRC
- (Via Microsoft) Good collection of EC, RS, LRC and related material
- (Via Microsoft) Storage Spaces Fault Tolerance
- (Via Microsoft) Better Way To Store Data with EC/LRC
- (Via Microsoft) Volume resiliency and efficiency in Storage Spaces
Shingled Erasure Code (SHEC)
Shingled Erasure Codes (SHEC) are a variation of Erasure Codes leveraging shingled overlay approach similar to what is being used in Shingled Magnetic Recording (SMR) on some HDDs. Ceph has been an early promoter of SHEC, read more here, and here.
Replication and Mirroring
Replication and Mirroring create a mirror or replica copy of data across different devices, systems, servers, clusters, sites or regions. In addition to keeping a copy, mirror and replication can occur on different time intervals such as real-time ( synchronous) and time deferred (Asynchronous). Besides time intervals, mirror and replication are implemented in different locations at various altitudes or stack layers from lower level hardware adapter or storage systems and appliances, to operating systems, hypervisors, software defined storage, volume managers, databases and applications themselves.
Covered in more detail in chapters 5 and 6, synchronous provides real-time, strong consistency, although high-latency local or remote interfaces can impact primary application performance. Note there is a common myth that high-latency networks are only long distance when in fact some local networks can also be high-latency. Asynchronous (also discussed in more depth in chapters 5 and 6) enables local and remote high-latency communications to be spanned, facilitating protection over a distance without impacting primary application performance, albeit with lower consistency, time deferred, also known as eventual consistency.
Mirroring (also known as RAID 1) and replication creates a copy (a mirror or replica) across two or more storage targets (devices, systems, file systems, cloud storage service, applications such as a database). The reason for using mirrors is to provide a faster (for normal running and during recovery) failure-tolerant mode for enabling availability, resiliency, and data protection, particularly for active data.
Figure 9.10 shows general replication scenarios. Illustrated are two basic mirror scenarios: At the top, a device, volume, file system, or object bucket is replicated to two other targets (i.e., three-way or three replicas); At the bottom, is a primary storage device using a hybrid replica and dispersal technique where multiple data chunks, shards, fragments, or extents are spread across devices in different locations.

Figure 9.10 Various Mirror and Replication Approaches
Mirroring and replication can be done locally inside a system (server, storage system, or appliance), within a cabinet, rack, or data center, or remotely, including at cloud services. Mirroring can also be implemented inside a server in software or using RAID and HBA cards to off-load the processing.

Figure 9.11 Mirror or Replication combined with Snapshots or other PiT protection
Keep in mind that mirroring and replication by themselves are not a replacement for backups, versions, snapshots, or another recovery point, time-interval (time-gap) protection. The reason is that replication and mirroring maintain a copy of the source at one or more destination targets. What this means is that anything that changes on the primary source also gets applied to the target destination (mirror or replica). However, it also means that anything changed, deleted, corrupted, or damaged on the source is also impacted on the mirror replica (assuming the mirror or replicas were or are mounted and accessible on-line).
implementations in various locations (hardware, software, cloud) include:
- Applications and databases such as SQL Server, Oracle among others
- File systems, volume manager, Software-defined storage managers
- Third-party storage software utilities and drivers
- Operating systems and hypervisors
- Hardware adapter and off-load devices
- Storage systems and appliances
- Cloud and managed services
Where To Learn More
Continue reading additional posts in this series of Data Infrastructure Data Protection fundamentals and companion to Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials (CRC Press 2017) book, as well as the following links covering technology, trends, tools, techniques, tradecraft and tips.
Additional learning experiences along with common questions (and answers), as well as tips can be found in Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials book.

What This All Means
There are various data protection technologies, tools and techniques for enabling availability of information resources including applications, data and data Infrastructure resources. Likewise there are many different aspects of RAID as well as context from legacy hardware based to cloud, virtual, container and software defined. In other words, not all RAID is in legacy storage systems, and there is a lot of FUD about RAID in general that is probably actually targeted more at specific implementations or products.
There are different approaches to meet various needs from stripe for performance with no protection by itself, to mirror and replication, as well as many parity approaches from legacy to erasure codes including Reed Solomon based as well as LRC among others. Which approach is best depends on your objects including balancing performance, availability, capacity economic (PACE) for normal running behavior as well as during faults and failure modes.
Get your copy of Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials here at Amazon.com, at CRC Press among other locations and learn more here. Meanwhile, continue reading with the next post in this series, Part 4 Data Protection Recovery Points (Archive, Backup, Snapshots, Versions).
Ok, nuff said, for now.
Gs
Greg Schulz – Microsoft MVP Cloud and Data Center Management, VMware vExpert 2010-2017 (vSAN and vCloud). Author of Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials (CRC Press), as well as Cloud and Virtual Data Storage Networking (CRC Press), The Green and Virtual Data Center (CRC Press), Resilient Storage Networks (Elsevier) and twitter @storageio. Courteous comments are welcome for consideration. First published on https://storageioblog.com any reproduction in whole, in part, with changes to content, without source attribution under title or without permission is forbidden.
All Comments, (C) and (TM) belong to their owners/posters, Other content (C) Copyright 2006-2026 Server StorageIO and UnlimitedIO. All Rights Reserved. StorageIO is a registered Trade Mark (TM) of Server StorageIO.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

