Application Data Value Characteristics Everything Is Not The Same

Application Data Value Characteristics Everything Is Not The Same
This is part one of a five-part mini-series looking at Application Data Value Characteristics Everything Is Not The Same as a companion excerpt from chapter 2 of my new book Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials – Cloud, Converged and Virtual Fundamental Server Storage I/O Tradecraft (CRC Press 2017). available at Amazon.com and other global venues. In this post, we start things off by looking at general application server storage I/O characteristics that have an impact on data value as well as access.

Everything is not the same across different organizations including Information Technology (IT) data centers, data infrastructures along with the applications as well as data they support. For example, there is so-called big data that can be many small files, objects, blobs or data and bit streams representing telemetry, click stream analytics, logs among other information.
Keep in mind that applications impact how data is accessed, used, processed, moved and stored. What this means is that a focus on data value, access patterns, along with other related topics need to also consider application performance, availability, capacity, economic (PACE) attributes.
If everything is not the same, why is so much data along with many applications treated the same from a PACE perspective?
Data Infrastructure resources including servers, storage, networks might be cheap or inexpensive, however, there is a cost to managing them along with data.
Managing includes data protection (backup, restore, BC, DR, HA, security) along with other activities. Likewise, there is a cost to the software along with cloud services among others. By understanding how applications use and interact with data, smarter, more informed data management decisions can be made.
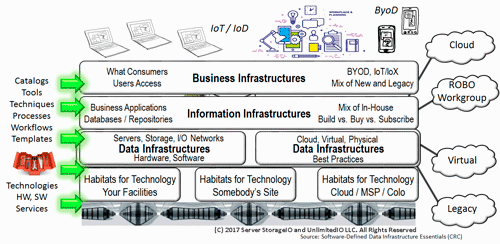
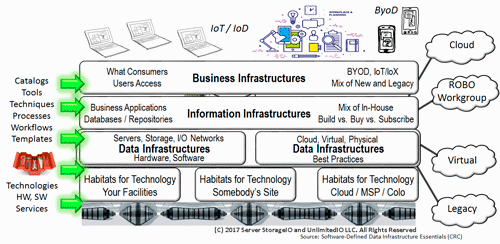
IT Applications and Data Infrastructure Layers
Keep in mind that everything is not the same across various organizations, data centers, data infrastructures, data and the applications that use them. Also keep in mind that programs (e.g. applications) = algorithms (code) + data structures (how data defined and organized, structured or unstructured).
There are traditional applications, along with those tied to Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), Big Data and other analytics including real-time click stream, media and entertainment, security and surveillance, log and telemetry processing among many others.
What this means is that there are many different application with various character attributes along with resource (server compute, I/O network and memory, storage requirements) along with service requirements.
Common Applications Characteristics
Different applications will have various attributes, in general, as well as how they are used, for example, database transaction activity vs. reporting or analytics, logs and journals vs. redo logs, indices, tables, indices, import/export, scratch and temp space. Performance, availability, capacity, and economics (PACE) describes the applications and data characters and needs shown in the following figure.
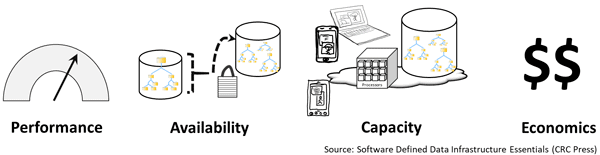
Application PACE attributes (via Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials)
All applications have PACE attributes, however:
- PACE attributes vary by application and usage
- Some applications and their data are more active than others
- PACE characteristics may vary within different parts of an application
Think of applications along with associated data PACE as its personality or how it behaves, what it does, how it does it, and when, along with value, benefit, or cost as well as quality-of-service (QoS) attributes.
Understanding applications in different environments, including data values and associated PACE attributes, is essential for making informed server, storage, I/O decisions and data infrastructure decisions. Data infrastructures decisions range from configuration to acquisitions or upgrades, when, where, why, and how to protect, and how to optimize performance including capacity planning, reporting, and troubleshooting, not to mention addressing budget concerns.
Primary PACE attributes for active and inactive applications and data are:
P – Performance and activity (how things get used)
A – Availability and durability (resiliency and data protection)
C – Capacity and space (what things use or occupy)
E – Economics and Energy (people, budgets, and other barriers)
Some applications need more performance (server computer, or storage and network I/O), while others need space capacity (storage, memory, network, or I/O connectivity). Likewise, some applications have different availability needs (data protection, durability, security, resiliency, backup, business continuity, disaster recovery) that determine the tools, technologies, and techniques to use.
Budgets are also nearly always a concern, which for some applications means enabling more performance per cost while others are focused on maximizing space capacity and protection level per cost. PACE attributes also define or influence policies for QoS (performance, availability, capacity), as well as thresholds, limits, quotas, retention, and disposition, among others.
Performance and Activity (How Resources Get Used)
Some applications or components that comprise a larger solution will have more performance demands than others. Likewise, the performance characteristics of applications along with their associated data will also vary. Performance applies to the server, storage, and I/O networking hardware along with associated software and applications.
For servers, performance is focused on how much CPU or processor time is used, along with memory and I/O operations. I/O operations to create, read, update, or delete (CRUD) data include activity rate (frequency or data velocity) of I/O operations (IOPS). Other considerations include the volume or amount of data being moved (bandwidth, throughput, transfer), response time or latency, along with queue depths.
Activity is the amount of work to do or being done in a given amount of time (seconds, minutes, hours, days, weeks), which can be transactions, rates, IOPs. Additional performance considerations include latency, bandwidth, throughput, response time, queues, reads or writes, gets or puts, updates, lists, directories, searches, pages views, files opened, videos viewed, or downloads.
Server, storage, and I/O network performance include:
- Processor CPU usage time and queues (user and system overhead)
- Memory usage effectiveness including page and swap
- I/O activity including between servers and storage
- Errors, retransmission, retries, and rebuilds
the following figure shows a generic performance example of data being accessed (mixed reads, writes, random, sequential, big, small, low and high-latency) on a local and a remote basis. The example shows how for a given time interval (see lower right), applications are accessing and working with data via different data streams in the larger image left center. Also shown are queues and I/O handling along with end-to-end (E2E) response time.
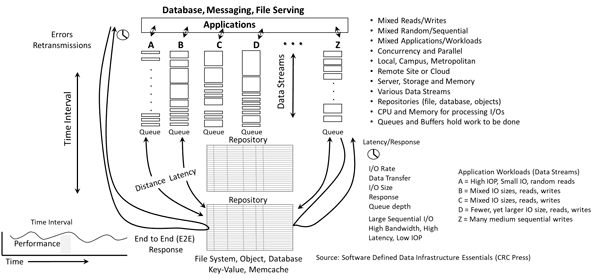
Server I/O performance fundamentals (via Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials)
Click here to view a larger version of the above figure.
Also shown on the left in the above figure is an example of E2E response time from the application through the various data infrastructure layers, as well as, lower center, the response time from the server to the memory or storage devices.
Various queues are shown in the middle of the above figure which are indicators of how much work is occurring, if the processing is keeping up with the work or causing backlogs. Context is needed for queues, as they exist in the server, I/O networking devices, and software drivers, as well as in storage among other locations.
Some basic server, storage, I/O metrics that matter include:
- Queue depth of I/Os waiting to be processed and concurrency
- CPU and memory usage to process I/Os
- I/O size, or how much data can be moved in a given operation
- I/O activity rate or IOPs = amount of data moved/I/O size per unit of time
- Bandwidth = data moved per unit of time = I/O size × I/O rate
- Latency usually increases with larger I/O sizes, decreases with smaller requests
- I/O rates usually increase with smaller I/O sizes and vice versa
- Bandwidth increases with larger I/O sizes and vice versa
- Sequential stream access data may have better performance than some random access data
- Not all data is conducive to being sequential stream, or random
- Lower response time is better, higher activity rates and bandwidth are better
Queues with high latency and small I/O size or small I/O rates could indicate a performance bottleneck. Queues with low latency and high I/O rates with good bandwidth or data being moved could be a good thing. An important note is to look at several metrics, not just IOPs or activity, or bandwidth, queues, or response time. Also, keep in mind that metrics that matter for your environment may be different from those for somebody else.
Something to keep in perspective is that there can be a large amount of data with low performance, or a small amount of data with high-performance, not to mention many other variations. The important concept is that as space capacity scales, that does not mean performance also improves or vice versa, after all, everything is not the same.
Where to learn more
Learn more about Application Data Value, application characteristics, PACE along with data protection, software defined data center (SDDC), software defined data infrastructures (SDDI) and related topics via the following links:
- Part 1 – Application Data Value Characteristics Everything Is Not The Same
- Part 2 – 4 3 2 1 Data Protection Application Data Availability
- Part 3 – Application Data Characteristics Types Everything Is Not The Same
- Part 4 – Application Data Volume Velocity Variety Everything Is Not The Same
- Part 5 – Application Data Access Life cycle Patterns Everything Not The Same
- Data Infrastructure server storage I/O network Recommended Reading
- World Backup Day 2018 Data Protection Readiness Reminder
- Data Infrastructure Server Storage I/O related Tradecraft Overview
- Data Infrastructure Overview, Its What’s Inside of Data Centers
- 4 3 2 1 and 3 2 1 data protection best practices
- Garbage data in, garbage information out, big data or big garbage?
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) Resources Are You Ready?
- Which Enterprise HDD to use for a Content Server Platform
- The SSD Place (SSD, NVM, PM, SCM, Flash, NVMe, 3D XPoint, MRAM and related topics)
- The NVMe Place (NVMe related topics, trends, tools, technologies, tip resources)
- Data Protection Diaries (Archive, Backup/Restore, BC, BR, DR, HA,Replication, Security)
Additional learning experiences along with common questions (and answers), as well as tips can be found in Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials book.

What this all means and wrap-up
Keep in mind that with Application Data Value Characteristics Everything Is Not The Same across various organizations, data centers, data infrastructures spanning legacy, cloud and other software defined data center (SDDC) environments. However all applications have some element (high or low) of performance, availability, capacity, economic (PACE) along with various similarities. Likewise data has different value at various times. Continue reading the next post (Part II Application Data Availability Everything Is Not The Same) in this five-part mini-series here.
Ok, nuff said, for now.
Gs
Greg Schulz – Microsoft MVP Cloud and Data Center Management, VMware vExpert 2010-2017 (vSAN and vCloud). Author of Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials (CRC Press), as well as Cloud and Virtual Data Storage Networking (CRC Press), The Green and Virtual Data Center (CRC Press), Resilient Storage Networks (Elsevier) and twitter @storageio. Courteous comments are welcome for consideration. First published on https://storageioblog.com any reproduction in whole, in part, with changes to content, without source attribution under title or without permission is forbidden.
All Comments, (C) and (TM) belong to their owners/posters, Other content (C) Copyright 2006-2026 Server StorageIO and UnlimitedIO. All Rights Reserved. StorageIO is a registered Trade Mark (TM) of Server StorageIO.
![]()
![]()