Dell Technology World 2018 Announcement Summary

This is part one of a five-part series about Dell Technology World 2018 announcement summary. Last week (April 30-May 3) I traveled to Las Vegas Nevada (LAS) to attend Dell Technology World 2018 (e.g., DTW 2018) as a guest of Dell (that is a disclosure btw). There were several announcements along with plenty of other activity from sessions, meetings, hallway and event networking taking place at Dell Technology World DTW 2018.
Major data infrastructure technology announcements include:
- PowerMax all-flash array (AFA) solid state device (SSD) NVMe storage system
- PowerEdge four-socket 2U and 4U rack servers
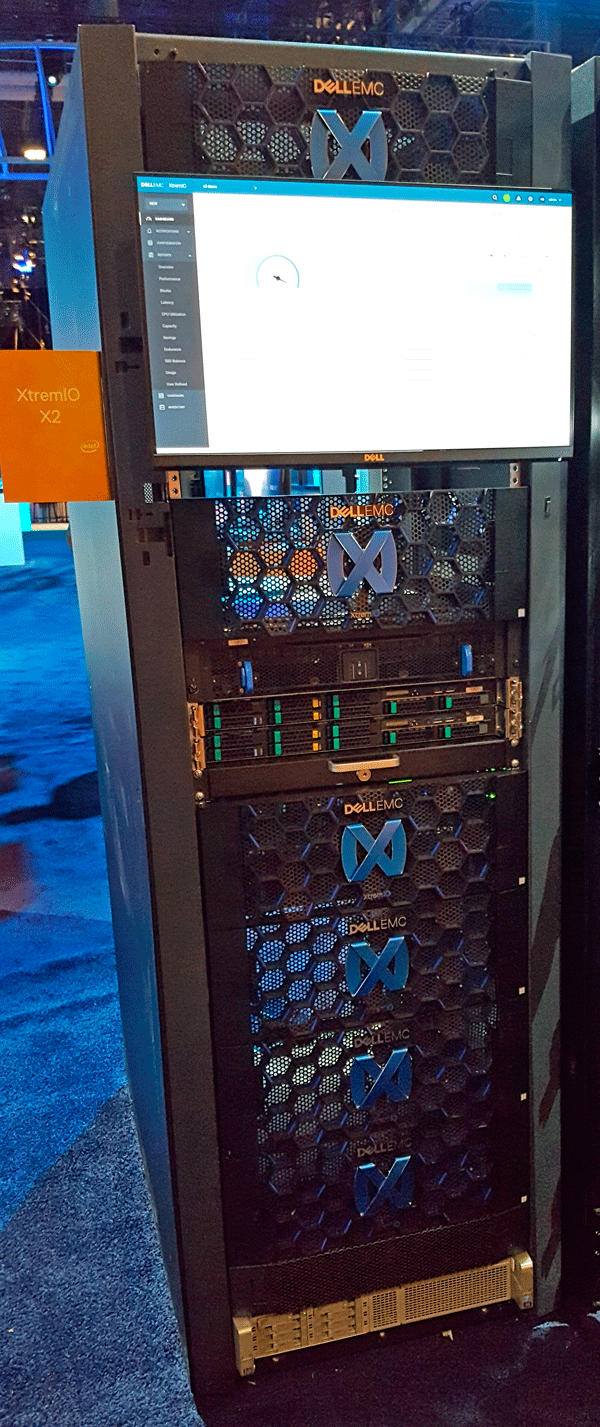
- XtremIO X2 AFA SSD storage system updates
- PowerEdge MX preview of future composable servers
- Desktop and thin client along with other VDI updates
- Cloud and networking enhancements
Besides the above, additional data infrastructure related announcements were made in association with Dell Technology family members including VMware along with other partners, as well as customer awards. Other updates and announcements were tied to business updates from Dell Technology, Dell Technical Capital (venture capital), and, Dell Financial Services.
Dell Technology World Buzzword Bingo Lineup
Some of the buzzword bingo terms, topics, acronyms from Dell Technology World 2018 included AFA, AI, Autonomous, Azure, Bare Metal, Big Data, Blockchain, CI, Cloud, Composable, Compression, Containers, Core, Data Analytics, Dedupe, Dell, DFS (Dell Financial Services), DFR (Data Footprint Reduction), Distributed Ledger, DL, Durability, Fabric, FPGA, GDPR, Gen-Z, GPU, HCI, HDD, HPC, Hybrid, IOP, Kubernetes, Latency, MaaS (Metal as a Service), ML, NFV, NSX, NVMe, NVMeoF, PACE (Performance Availability Capacity Economics), PCIe, Pivotal, PMEM, RAID, RPO, RTO, SAS, SATA, SC, SCM, SDDC, SDS, Socket, SSD, Stamp, TBW (Terabytes Written per day), VDI, venture capital, VMware and VR among others.

Dell Technology World DTW 2018 Event and Venue
Dell Technology World 2018 was located at the combined Palazzo and Venetian hotels along with adjacent Sands Expo center kicking off Monday, April 30th and wrapping up May 4th.
The theme for Dell Technology World DTW 2018 was make it real, which in some ways was interesting given the focus on virtual including virtual reality (VR), software-defined data center (SDDC) virtualization, data infrastructure topics, along with artificial intelligence (AI).

Make it real – Venetian Palazzo St. Mark’s Square on the way to Sands Expo Center
There was plenty of AI, VR, SDDC along with other technologies, tools as well as some fun stuff to do including VR games.

Dell Technology World Village Area near Key Note and Expo Halls

Dell Technology World Drone Flying Area
During a break from some meetings, I used a few minutes to fly a drone using VR which was interesting. I Have been operating drones (See some videos here) visually without dependence on first-person view (FPV) or relying on extensive autonomous operations instead flying heads up by hand for several years. Needless to say, the VR was interesting, granted encountered a bit of vertigo that I had to get used to.

More views of the Dell Technology World Village and Commons Area with VR activity

Dell Technology World Village and VR area

Dell Technology World Bean Bag Area
Dell Technology World 2018 Announcement Summary
Ok, nuff with the AI, ML, DL, VR fun, time to move on to the business and technology topics of Dell Technologies World 2018.
What was announced at Dell Technology World 2018 included among others:
- Dell Technologies World 2018 keynote kick off by Michael Dell
- Partner business growth for Dell Technologies with broader offerings and incentives
- Dell Technologies Capital (venture capital) first year out of stealth progress
- Customer award winners of Dell Technologies
- Dell PowerMax next-generation enterprise-class tier 0 and tier 1 storage system
- XtremIO X2 native replication and new lower cost entry model
- Dell EMC VxBlock System 1000 with PowerMax and XtremIO X2
- Dell PowerEdge R840 and R940xa rack servers
- Dell Wyse 5070 thin clients and new VDI solutions
- Microsoft Azure IoT, VMware Pulse IoT Center, and Dell edge solutions

Dell PowerMax Front View
Subsequent posts in this series take a deeper look at the various announcements as well as what they mean.
Where to learn more
Learn more about Dell Technology World 2018 and related topics via the following links:
- Dell Technology World 2018 Part I, Part II, Part III, Part IV and Part V
- Application Data Availability 4 3 2 1 Data Protection
- Application Data Value Characteristics Everything Is Not The Same (Part I)
- Data Infrastructure Primer Overview (Its Whats Inside The Data Center)
- Dell EMC Expands Server Capabilities for Software-defined, Edge and High-Performance Computing (e.g., AMD EPYC)
- Dell EMC World 2017 Day One news announcement summary
- Have you heard about the new CLOUD Act data regulation?
- HPE Announces AMD Powered Gen 10 ProLiant DL385 For Software Defined
- If NVMe is the answer, what are the questions?
- New family of Intel Xeon Scalable Processors enable software defined data infrastructures (SDDI) and SDDC
- NVMe Primer (or refresh) and The NVMe Place (e.g., https://storageioblog.com/nvme-place-volatile-memory-express/)
- PCIe Fundamentals Server Storage I/O Network Essentials
- The SSD Place (e.g., https://storageioblog.com/nand-flash-ssd-storage-io-conversation/) nand flash, SCM, and related topics
- Via SearchStorage: Dell EMC all-flash PowerMax replaces VMAX, injects NVMe
- Via SearchStorage: Dell EMC midrange storage keeps its overlapping arrays
- Via SearchStorage: Dell EMC storage IPO, VMware merger plans still unclear
- Via SearchStorage: Dell EMC storage strategy talk buzzes Dell Tech World
- Via SearchStorage: How a Dell and VMware merger could affect EMC storage
- VMware continues cloud construction with March announcements
- VMware vSphere vSAN vCenter version 6.7 SDDC Update Summary
- Hot Popular New Trending Data Infrastructure Vendors To Watch
- Data Infrastructure server storage I/O network Recommended Reading
- Data Infrastructure Overview, Its What’s Inside of Data Centers
Additional learning experiences along with common questions (and answers), as well as tips can be found in Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials book.
What this all means
On the surface it may appear that there was not much announced at Dell Technology World 2018 particular compared to some of the recent Dell EMC Worlds and EMC Worlds. However turns out that there was a lot announced, granted without some of the entertainment and circus like atmosphere of previous events. Continue reading here Part II Dell Technology World 2018 Modern Data Center Announcement Details in this series, along with Part III here, Part IV here (including PowerEdge MX composable infrastructure leveraging Gen-Z) and Part V (servers and converged) here.
Ok, nuff said, for now.
Cheers Gs
Greg Schulz – Microsoft MVP Cloud and Data Center Management, VMware vExpert 2010-2017 (vSAN and vCloud). Author of Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials (CRC Press), as well as Cloud and Virtual Data Storage Networking (CRC Press), The Green and Virtual Data Center (CRC Press), Resilient Storage Networks (Elsevier) and twitter @storageio. Courteous comments are welcome for consideration. First published on https://storageioblog.com any reproduction in whole, in part, with changes to content, without source attribution under title or without permission is forbidden.
All Comments, (C) and (TM) belong to their owners/posters, Other content (C) Copyright 2006-2024 Server StorageIO and UnlimitedIO. All Rights Reserved. StorageIO is a registered Trade Mark (TM) of Server StorageIO.