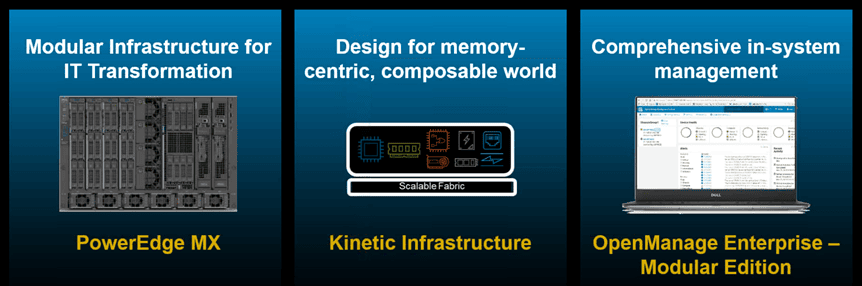
Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 Kinetic Based Data Infrastructure Architecture

Dell EMC today announced with a tag line IT Unbound their new PowerEdge MX 7000 Kinetic Based Data Infrastructure Architecture slated for general availability September 21, 2018. Previewed earlier this year at Dell Technology World in Las Vegas, PowerEdge MX 7000 is a new family of modular, scalable servers for various data infrastructure roles.
What is different with PowerEdge MX 7000 compared to other new 14th generation (Gen 14) Dell servers is the finer granularity of resource allocation based around the new Kinetic composable infrastructure. Also previewed at Dell Technology World earlier this year in Las Vegas, Kinetic (not to be confused the Seagate Kinetic object storage key value drive initiative) is a new composable architecture.
Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 Kinetic What Was Announced
- First instantiation of Kinetic composable based data infrastructure resources
- OpenManage Enterprise Modular Edition
- PowerEdge MX 7000 modular data infrastructure server
Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 and Kinetic Architecture Image via Dell.com
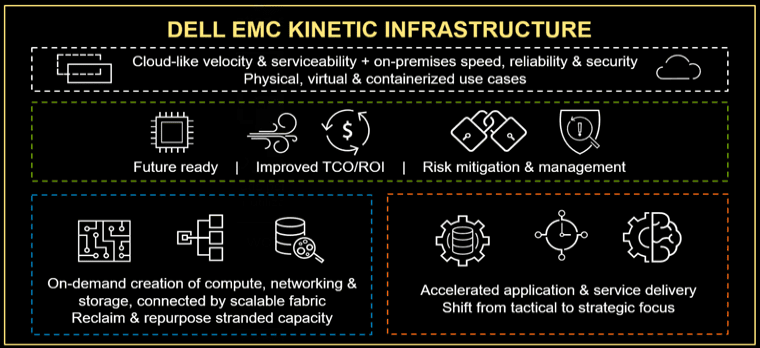
Dell EMC Kinetic Composability What Is It
By being a composable data infrastructure resource and server, Dell EMC Kinetic based solutions can be decomposed with finer granularity than previous servers. What this means is that in the past, memory, I/O network, physical storage devices, compute sockets and cores were assigned to a single image instance. The only image instance could be an operating system (OS) such as Linux or Windows based, a hypervisor such as KVM, Microsoft Hyper-V, Nitro (AWS), Oracle, VMware vSphere ESXi, or Xen among others, as well as proprietary decomposition and aggregation software (and hardware) technology (ScaleMP among others).
With a composable based solution, instead of the entire server, or motherboard(s) and its resources allocated to a single OS as a bare metal (BM) or Metal as a Service (MaaS) instance, or to a hypervisor, different resources can be allocated to various instances. On the surface it would be easy to say that sounds a lot like what hypervisors such as those from Microsoft, VMware, and others are doing, particular with clusters.
Dell EMC Kinetic Data Infrastructure Architecture Image via Dell.com
However, the difference is that with hypervisors, all of a server’s physical resources (compute, memory, I/O, storage devices, GPU, FPGA/ASIC) are allocated to the OS, hypervisor, or composition software, that then creates vCPU, vRAM, and related resources. Emphasis is on enabling more granular resource allocation as well as scaling out. The business or organizational outcome is what is essential which means, better allocation and effective use of resources to boost productivity vs. merely driving up utilization and efficiency.
Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 Eliminates traditional hardware-based mid-plane with an internal fabric connector per node that can also be exposed outside of the physical MX enclosure. By using an industry standard connector on the edge of server motherboard resource nodes, different server I/O connectivity can be leveraged as it becomes available or improves. For example, IMHO it is not too complicated to envision a time in the not so distant future when Kinetic enabled resources (e.g., server nodes) evolve to support the emerging Gen-Z server I/O connectivity protocol.
What is Gen-Z
Does PowerEdge MX 7000 and Kinetic use Gen-Z today? Not yet, however, Dell has been showing demos and technology proof of concepts at various events.
Why bring up Gen-Z now? Simple, it’s something that will be part of many data infrastructure, the server I/O, storage, networking, hardware and software-defined discussions in the not so distant future.
As a refresher or primer, Gen-Z is a new server I/O fabric interface that supports access of and by CPU sockets along with their cores or memory including DRAM as well as emerging SCM as well as PMEM. In addition to server memory access. Gen-Z also enables local as well as remote access to memory, storage, GPU, FPGA, ASIC among other resources. For backward compatibility as well as investment protection, Gen-Z is intended to work with existing PCIe, Ethernet, Fibre Channel, SAS, SATA, NVMe, InfiniBand among another server I/O interconnects and protocols.
Does this mean Gen-Z is a challenger for Ethernet and another IP-based general LAN networking? IMHO no, at least not in the foreseeable future, granted like PCIe, Fibre Channel, InfiniBand, Ethernet and some others that have joined the where are they now list of technologies that promised to be the end all network for everything, near-term Gen-Z is focused on inside a modular enclosure or perhaps within a rack. Read more about Gen-Z here, as well as Dell EMC blog The Gen-Z Journey road to composability.
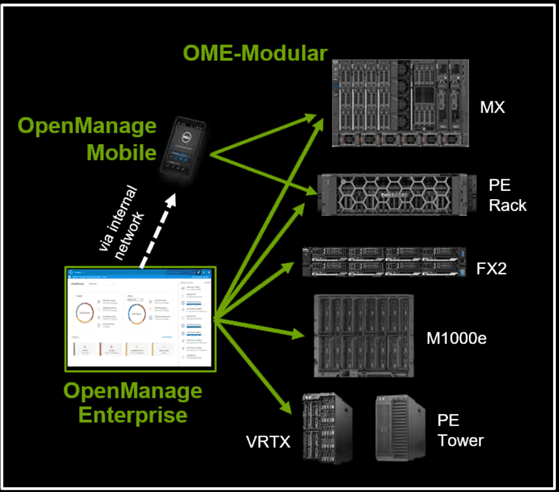
Dell OpenManage Management Interface Image via Dell.com
OpenManage Enterprise Modular Edition
Management for PowerEdge MX 7000 utilizes OpenManage Enterprise Modular Edition that is an HTML5 REST based with API tool. Management capabilities include workflow’s for simplicity of operation and lifecycle management. OpenManage Enterprise Module Edition besides being HTML5 REST API is also RedFish inspired for further interoperability. Note that PowerEdge MX 7000 is also integrated with Dell iDRAC physical machine level management interface provides unified management from a single to multiple server groups spanning towers to racks.

Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 Image via Dell.com
Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 Kinetic Based Data Infrastructure Server
The new Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 is the first installment of their new Kinetic based composable architecture. The new Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 components consist of a 7U chassis with power and cooling fans, along with compute sled, storage sled, I/O connectivity and inner fabric, along with management tools.

Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 Modules Image via Dell.com
Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 Server Compute modules
Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 Compute sleds include MX740c (single width) and MX840c (double width) that are two and four socket modules with local on-board NVMe (e.g., U.2 8639 small form factor SFF) drives (per module). These initial compute modules support Intel Xeon processors and up to six (6) TBytes of memory. The MX740c supports up to six (6) local NVMe, SAS or SATA drives (e.g., 8639 connectors), while the MX840c supports up to eight (8) local drives. Note that these local onboard drives can be shared with other sled modules, as well as compute sleds can access the shared storage sled-based drives.
Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 Server Storage modules
Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 Storage sled consists of MX5016s holding up to 16 hot-pluggable SAS HDD, up to seven MX5016s sleds can be configured per MX chassis for up to 112 direct attached storage (DAS) drives. Each of the drives can be individually mapped to one or more servers supporting aggregated (e.g., HCI) as well as disaggregated (CI and legacy) deployment topologies.
Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 Server I/O Networking Modules
Initial server I/O modules for the new Dell EMC PowerEdge MX include 25GbE and 32G Fibre Channel (GFC) host connectivity along with 100GbE and 32 GFC uplink capabilities with the top of rack (ToR)support built in along with Open Networking OS10EE software enabled. The server I/O modules provide both north-south, as well as east-west connectivity inside and outside the chassis for data plane and management plane traffic.
Server I/O connectivity options include:
- MX5108n Ethernet Switch with 8 x 25GbE (server facing ports), 2 x 100GbE ports, 1 x 40GbE port, 4 x 10GbE ports.
- MX9116n Fabric Switching Engine (e.g., Kinetic fabric) with 16 x 25GbE server facing ports, 2 x 100GbE/8 x 32GFC unified ports, 2 x 100 GbE ports and 12 fabric expansion ports.
- MXG610s Fibre Channel Switch with 16 x 32GFC internal ports, 8 x 32 GFC SFP+ ports and 2 QSFP (4 x 32GFC) uplink ports.
Where to learn more
Learn more about Dell EMC PowerEdge MX, Kinetic, Composable and data infrastructures related topics via the following links:
- Meet PowerEdge MX, the First Platform Designed with Kinetic Infrastructure (Dell EMC Blog)
- Dell EMC Launches PowerEdge MX, Offering Agile, Flexible, Modular Infrastructure for IT Transformation (Dell EMC PR)
- Kinetic Infrastructure is the Path to Full Composability (Dell EMC Blog)
- The Gen-Z Journey: The Road to Full Composability (Dell EMC Blog)
- Dell Technologies Announces Class V VMware Tracking Stock exchange for stock or cash
- Dell Technology World 2018 Part I, Part II, Part III, Part IV and Part V
- July 2018 Server StorageIO Data Infrastructure Update Newsletter
- June 2018 Server StorageIO Data Infrastructure Update Newsletter
- 2018 Hot Popular New Trending Data Infrastructure Vendors to Watch
- Application Data Value Characteristics Everything Is Not The Same (Part I)
- Data Infrastructure Primer Overview (Its What’s Inside The Data Center)
- If NVMe is the answer, what are the questions?
- Catching Up With Summer 2018 IBM Cloudy Software Defined Storage Announcements
- Server StorageIO 2018 VMworld Data Infrastructure Buzzword Bingo Puzzle
- NVMe Primer (or refresh), The NVMe Place, The SSD Place, and the Object Storage Center
- Data Infrastructure server storage I/O network Recommended Reading
Additional learning experiences along with common questions (and answers), as well as tips can be found in Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials book.

What this all means
Overall this is a good announcement of technology, product, as well as where resources are headed to meet different workload demands and look forward to getting some test time with a Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000.
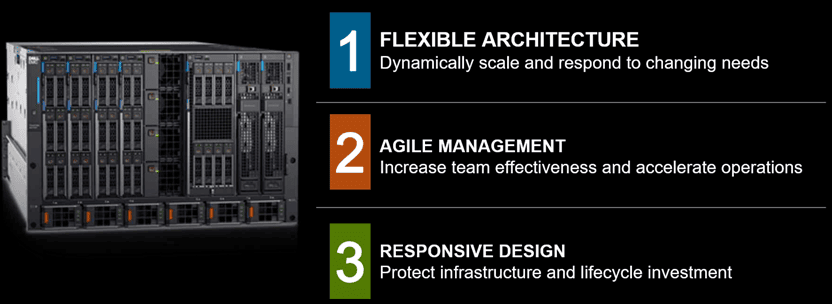
Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 Three Tenants Image via Dell.com
The new Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 Provides a data infrastructure resource platform for deploying traditional, cloud, software-defined, composable, as well as converged infrastructure (CI) disaggregated, as well as hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) aggregated along with hybrid configurations.
With the Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000, there is more resource granularity and future-proof capabilities than traditional high-density blade, as well as twin, quad or eight node server configuration solutions.
Many vendors talk about solutions being future proof or enabling investment protection, with PowerEdge MX 7000, Dell EMC is taking the next step in discussing trends, technology, and what you can do today. Unlike traditional dual, quad, eight or high-density node and blade servers with dedicated discrete mid-planes tied to a given technology, Dell PowerEdge MX 7000 and Kinetic based architecture are mid planes aka back plane free. Now there is still connectivity between the different PowerEdge MX 7000 chassis modules which is a fabric (network if you prefer).
For example, server compute sled modules have an industry standard connector that connects with other components in the chassis. What differs from the traditional blade and multi-node server configurations is that on board the compute sleds; an adapter module can be changed to support a new interface over different generations of technology (as an example, keep an eye on what happens with Gen-Z).
The result is that the Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 should be an excellent platform for software-defined data centers (SDDC), software-defined data infrastructures (SDDI), software-defined infrastructures (SDI) as well as other software defined or traditional deployments. The Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 will make for a good CI, HCI, SDDC, SDDI, SDI platform for public, private as well as hybrid clouds, PaaS as well as IaaS deployments, along with VMware, Microsoft (Hyper-V, Windows Storage Spaces Direct (S2D), as well as Azure Stack) among other scenarios.
By being flexible, scalable, agile and adaptable, easy management, responsive design that is future proof enabling a pool of dynamic data infrastructure resource, the Dell EMC PowerEdge MX 7000 should be good allowing IT Unbound.
Ok, nuff said, for now.
Cheers Gs
Greg Schulz – Microsoft MVP Cloud and Data Center Management, VMware vExpert 2010-2018. Author of Software Defined Data Infrastructure Essentials (CRC Press), as well as Cloud and Virtual Data Storage Networking (CRC Press), The Green and Virtual Data Center (CRC Press), Resilient Storage Networks (Elsevier) and twitter @storageio. Courteous comments are welcome for consideration. First published on https://storageioblog.com any reproduction in whole, in part, with changes to content, without source attribution under title or without permission is forbidden.
All Comments, (C) and (TM) belong to their owners/posters, Other content (C) Copyright 2006-2026 Server StorageIO and UnlimitedIO. All Rights Reserved. StorageIO is a registered Trade Mark (TM) of Server StorageIO.
![]()