This is an excerpt blog version of the popular Server and StorageIO Group white paper "IT Data Center and Data Storage Bottlenecks" originally published August of 2006 that is as much if not more relevant today than it was in the past.
Most Information Technology (IT) data centers have bottleneck areas that impact application performance and service delivery to IT customers and users. Possible bottleneck locations shown in Figure-1 include servers (application, web, file, email and database), networks, application software, and storage systems. For example users of IT services can encounter delays and lost productivity due to seasonal workload surges or Internet and other network bottlenecks. Network congestion or dropped packets resulting in wasteful and delayed retransmission of data can be the results of network component failure, poor configuration or lack of available low latency bandwidth.
Server bottlenecks due to lack of CPU processing power, memory or under sized I/O interfaces can result in poor performance or in worse case scenarios application instability. Application including database systems bottlenecks due to excessive locking, poor query design, data contention and deadlock conditions result in poor user response time. Storage and I/O performance bottlenecks can occur at the host server due to lack of I/O interconnect bandwidth such as an overloaded PCI interconnect, storage device contention, and lack of available storage system I/O capacity.
These performance bottlenecks, impact most applications and are not unique to the large enterprise or scientific high compute (HPC) environments. The direct impact of data center I/O performance issues include general slowing of the systems and applications, causing lost productivity time for users of IT services. Indirect impacts of data center I/O performance bottlenecks include additional management by IT staff to trouble shoot, analyze, re-configure and react to application delays and service disruptions.
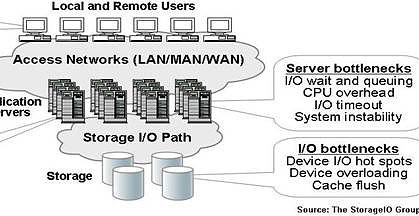
Figure-1: Data center performance bottleneck locations
Data center performance bottleneck impacts (see Figure-1) include:
- Under utilization of disk storage capacity to compensate for lack of I/O performance capability
- Poor Quality of Service (QoS) causing Service Level Agreements (SLA) objectives to be missed
- Premature infrastructure upgrades combined with increased management and operating costs
- Inability to meet peak and seasonal workload demands resulting in lost business opportunity
I/O bottleneck impacts
It should come as no surprise that businesses continue to consume and rely upon larger amounts of disk storage. Disk storage and I/O performance fuel the hungry needs of applications in order to meet SLAs and QoS objectives. The Server and StorageIO Group sees that, even with efforts to reduce storage capacity or improve capacity utilization with information lifecycle management (ILM) and Infrastructure Resource Management (IRM) enabled infrastructures, applications leveraging rich content will continue to consume more storage capacity and require additional I/O performance. Similarly, at least for the next few of years, the current trend of making and keeping additional copies of data for regulatory compliance and business continue is expected to continue. These demands all add up to a need for more I/O performance capabilities to keep up with server processor performance improvements.
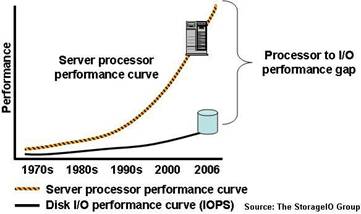
Figure-2: Processing and I/O performance gap
Server and I/O performance gap
The continued need for accessing more storage capacity results in an alarming trend: the expanding gap between server processing power and available I/O performance of disk storage (Figure-2). This server to I/O performance gap has existed for several decades and continues to widen instead of improving. The net impact is that bottlenecks associated with the server to I/O performance lapse result in lost productivity for IT personal and customers who must wait for transactions, queries, and data access requests to be resolved.
Application symptoms of I/O bottlenecks
There are many applications across different industries that are sensitive to timely data access and impacted by common I/O performance bottlenecks. For example, as more users access a popular file, database table, or other stored data item, resource contention will increase. One way resource contention manifests itself is in the form of database “deadlock” which translates into slower response time and lost productivity.
Given the rise and popularity of internet search engines, search engine optimization (SEO) and on-line price shopping, some businesses have been forced to create expensive read-only copies of databases. These read-only copies are used to support more queries to address bottlenecks from impacting time sensitive transaction databases.
In addition to increased application workload, IT operational procedures to manage and protect data help to contribute to performance bottlenecks. Data center operational procedures result in additional file I/O scans for virus checking, database purge and maintenance, data backup, classification, replication, data migration for maintenance and upgrades as well as data archiving. The net result is that essential data center management procedures contribute to performance challenges and impacting business productivity.
Poor response time and increased latency
Generally speaking, as additional activity or application workload including transactions or file accesses are performed, I/O bottlenecks result in increased response time or latency (shown in Figure-3). With most performance metrics more is better; however, in the case of response time or latency, less is better. Figure-3 shows the impact as more work is performed (dotted curve) and resulting I/O bottlenecks have a negative impact by increasing response time (solid curve) above acceptable levels. The specific acceptable response time threshold will vary by applications and SLA requirements. The acceptable threshold level based on performance plans, testing, SLAs and other factors including experience serves as a guide line between acceptable and poor application performance.
As more workload is added to a system with existing I/O issues, response time will correspondingly decrease as was seen in Figure-3. The more severe the bottleneck, the faster response time will deteriorate (e.g. increase) from acceptable levels. The elimination of bottlenecks enables more work to be performed while maintaining response time below acceptable service level threshold limits.
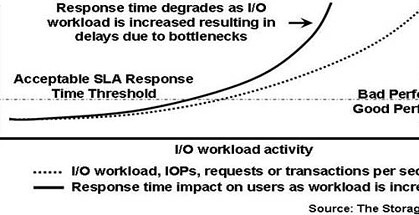
Figure-3: I/O response time performance impact
Seasonal and peak workload I/O bottlenecks
Another common challenge and cause of I/O bottlenecks is seasonal and/or unplanned workload increases that result in application delays and frustrated customers. In Figure-4 a workload representing an eCommerce transaction based system is shown with seasonal spikes in activity (dotted curve). The resulting impact to response time (solid curve) is shown in relation to a threshold line of acceptable response time performance. For example, peaks due holiday shopping exchanges appear in January then dropping off increasing near mother’s day in May, then back to school shopping in August results in increased activity as does holiday shopping starting in late November.
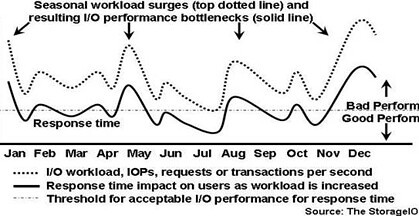
Figure-4: I/O bottleneck impact from surge workload activity
Compensating for lack of performance
Besides impacting user productivity due to poor performance, I/O bottlenecks can result in system instability or unplanned application downtime. One only needs to recall recent electric power grid outages that were due to instability, insufficient capacity bottlenecks as a result of increased peak user demand.
I/O performance improvement approaches to address I/O bottlenecks have been to do nothing (incur and deal with the service disruptions) or over configure by throwing more hardware and software at the problem. To compensate for lack of I/O performance and counter the resulting negative impact to IT users, a common approach is to add more hardware to mask or move the problem.
However, this often leads to extra storage capacity being added to make up for a short fall in I/O performance. By over configuring to support peak workloads and prevent loss of business revenue, excess storage capacity must be managed throughout the non-peak periods, adding to data center and management costs. The resulting ripple affect is that now more storage needs to be managed, including allocating storage network ports, configuring, tuning, and backing up of data. This can and does result in environments that have storage utilization well below 50% of their useful storage capacity. The solution is to address the problem rather than moving and hiding the bottleneck elsewhere (rather like sweeping dust under the rug).
Business value of improved performance
Putting a value on the performance of applications and their importance to your business is a necessary step in the process of deciding where and what to focus on for improvement. For example, what is the value of reducing application response time and the associated business benefit of allowing more transactions, reservations or sales to be made? Likewise, what is the value of improving the productivity of a designer or animator to meet tight deadlines and market schedules? What is business benefit of enabling a customer to search faster for and item, place an order, access media rich content, or in general improve their productivity?
Server and I/O performance gap as a data center bottleneck
I/O performance bottlenecks are a wide spread issue across most data centers, affecting many applications and industries. Applications impacted by data center I/O bottlenecks to be looked at in more depth are electronic design automation (EDA), entertainment and media, database online transaction processing (OLTP) and business intelligence. These application categories represent transactional processing, shared file access for collaborative work, and processing of shared, time sensitive data.
Electronic design
Computer aided design (CAD), computer assisted engineering (CAE), electronic design automaton (EDA) and other design tools are used for a wide variety of engineering and design functions. These design tools require fast access to shared, secured and protected data. The objective of using EDA and other tools is to enable faster product development with better quality and improved worker productivity. Electronic components manufactured for the commercial, consumer and specialized markets rely on design tools to speed the time-to-market of new products as well as to improve engineer productivity.
EDA tools, including those from Cadence, Synopsis, Mentor Graphics and others, are used to develop expensive and time sensitive electronic chips, along with circuit boards and other components to meet market windows and suppler deadlines. An example of this is a chip vendor being able to simulate, develop, test, produce and deliver a new chip in time for manufacturers to release their new products based on those chips. Another example is aerospace and automotive engineering firms leveraging design tools, including CATIA and UGS, on a global basis relying on their suppler networks to do the same in a real-time, collaborative manner to improve productivity and time-to-market. These results in contention of shared file and data access and, as a work-around, more copies of data kept as local buffers.
I/O performance impacts and challenges for EDA, CAE and CAD systems include:
- Delays in drawing and file access resulting in lost productivity and project delays
- Complex configurations to support computer farms (server grids) for I/O and storage performance
- Proliferation of dedicated storage on individual servers and workstations to improve performance
Entertainment and media
While some applications are characterized by high bandwidth or throughput, such as streaming video and digital intermediate (DI) processing of 2K (2048 pixels per line) and 4K (4096 pixels per line) video and film, there are many other applications that are also impacted by I/O performance time delays. Even bandwidth intensive applications for video production and other applications are time sensitive and vulnerable to I/O bottleneck delays. For example, cell phone ring tone, instant messaging, small MP3 audio, and voice- and e-mail are impacted by congestion and resource contention.
Prepress production and publishing requiring assimilation of many small documents, files and images while undergoing revisions can also suffer. News and information websites need to look up breaking stories, entertainment sites need to view and download popular music, along with still images and other rich content; all of this can be negatively impacted by even small bottlenecks. Even with streaming video and audio, access to those objects requires accessing some form of a high speed index to locate where the data files are stored for retrieval. These indexes or databases can become bottlenecks preventing high performance storage and I/O systems from being fully leveraged.
Index files and databases must be searched to determine the location where images and objects, including streaming media, are stored. Consequently, these indices can become points of contention resulting in bottlenecks that delay processing of streaming media objects. When cell phone picture is taken phone and sent to someone, chances are that the resulting image will be stored on network attached storage (NAS) as a file with a corresponding index entry in a database at some service provider location. Think about what happens to those servers and storage systems when several people all send photos at the same time.
I/O performance impacts and challenges for entertainment and media systems include:
- Delays in image and file access resulting in lost productivity
- Redundant files and storage local servers to improve performance
- Contention for resources causing further bottlenecks during peak workload surges
OLTP and business intelligence
Surges in peak workloads result in performance bottlenecks on database and file servers, impacting time sensitive OLTP systems unless they are over configured for peak demand. For example, workload spikes due to holiday and back-to-school shopping, spring break and summer vacation travel reservations, Valentines or Mothers Day gift shopping, and clearance and settlement on peak stock market trading days strain fragile systems. For database systems maintaining performance for key objects, including transaction logs and journals, it is important to eliminate performance issues as well as maintain transaction and data integrity.
An example tied to eCommerce is business intelligence systems (not to be confused with back office marketing and analytics systems for research). Online business intelligence systems are popular with online shopping and services vendors who track customer interests and previous purchases to tailor search results, views and make suggestions to influence shopping habits.
Business intelligence systems need to be fast and support rapid lookup of history and other information to provide purchase histories and offer timely suggestions. The relative performance improvements of processors shift the application bottlenecks from the server to the storage access network. These applications have, in some cases, resulted in an exponential increase in query or read operations beyond the capabilities of single database and storage instances, resulting in database deadlock and performance problems or the proliferation of multiple data copies and dedicated storage on application servers.
A more recent contribution to performance challenges, caused by the increased availability of on-line shopping and price shopping search tools, is low cost craze (LCC) or price shopping. LCC has created a dramatic increase in the number of read or search queries taking place, further impacting database and file systems performance. For example, an airline reservation system that supports price shopping while preventing impact to time sensitive transactional reservation systems would create multiple read-only copies of reservations databases for searches. The result is that more copies of data must be maintained across more servers and storage systems thus increasing costs and complexity. While expensive, the alternative of doing nothing results in lost business and market share.
I/O performance impacts and challenges for OLTP and business intelligence systems include:
- Application and database contention, including deadlock conditions, due to slow transactions
- Disruption to application servers to install special monitoring, load balance or I/O driver software
- Increased management time required to support additional storage needed as a I/O workaround
Summary/Conclusion
It is vital to understand the value of performance, including response time or latency, and numbers of I/O operations for each environment and particular application. While the cost per raw TByte may seem relatively in-expensive, the cost for I/O response time performance also needs to be effectively addressed and put into the proper context as part of the data center QoS cost structure.
There are many approaches to address data center I/O performance bottlenecks with most centered on adding more hardware or addressing bandwidth or throughput issues. Time sensitive applications depend on low response time as workload including throughput increase and thus latency can not be ignored. The key to removing data center I/O bottlenecks is to find and address the problem instead of simply moving or hiding it with more hardware and/or software. Simply adding fast devices such as SSD may provide relief, however if the SSDs are attached to high latency storage controllers, the full benefit may not be realized. Thus, identify and gain insight into data center and I/O bottleneck paths eliminating issues and problems to boost productivity and efficiency.
Where to Learn More
Additional information about IT data center, server, storage as well as I/O networking bottlenecks along with solutions can be found at the Server and StorageIO website in the tips, tools and white papers, as well as news, books, and activity on the events pages. If you are in the New York area on September 23, 2009, check out my presentation on The Other Green – Storage Optimization and Efficiency that will touch on the above and other related topics. Download your copy of "IT Data Center and Storage Bottlenecks" by clicking here.
Ok, nuff said.
Cheers gs
Greg Schulz – Author Cloud and Virtual Data Storage Networking (CRC Press), The Green and Virtual Data Center (CRC Press) and Resilient Storage Networks (Elsevier)
twitter @storageio
All Comments, (C) and (TM) belong to their owners/posters, Other content (C) Copyright 2006-2026 Server StorageIO and UnlimitedIO LLC All Rights Reserved

