This post builds on a recent article I did that can be read here.
Even with tough economic times, there is no such thing as a data recession! Thus the importance of optimizing data storage efficiency addressing both performance and capacity without impacting availability in a cost effective way to do more with what you have.
What this means is that even though budgets are tight or have been cut resulting in reduced spending, overall net storage capacity is up year over year by double digits if not higher in some environments.
Consequently, there is continued focus on stretching available IT and storage related resources or footprints further while eliminating barriers or constraints. IT footprint constraints can be physical in a cabinet or rack as well as floorspace, power or cooling thresholds and budget among others.
Constraints can be due to lack of performance (bandwidth, IOPS or transactions), poor response time or lack of availability for some environments. Yet for other environments, constraints can be lack of capacity, limited primary or standby power or cooling constraints. Other constraints include budget, staffing or lack of infrastructure resource management (IRM) tools and time for routine tasks.
Look before you leap
Before jumping into an optimization effort, gain insight if you do not already have it as to where the bottlenecks exist, along with the cause and effect of moving or reconfiguring storage resources. For example, boosting capacity use to more fully use storage resources can result in a performance issue or data center bottlenecks for other environments.
An alternative scenario is that in the quest to boost performance, storage is seen as being under-utilized, yet when capacity use is increased, low and behold, response time deteriorates. The result can be a vicious cycle hence the need to address the issue as opposed to moving problems by using tools to gain insight on resource usage, both space and activity or performance.
Gaining insight means looking at capacity use along with performance and availability activity and how they use power, cooling and floor-space. Consequently an important tool is to gain insight and knowledge of how your resources are being used to deliver various levels of service.
Tools include storage or system resource management (SRM) tools that report on storage space capacity usage, performance and availability with some tools now adding energy usage metrics along with storage or system resource analysis (SRA) tools.
Cooling Off
Power and cooling are commonly talked about as constraints, either from a cost standpoint, or availability of primary or secondary (e.g. standby) energy and cooling capacity to support growth. Electricity is essential for powering IT equipment including storage enabling devices to do their specific tasks of storing data, moving data, processing data or a combination of these attributes.
Thus, power gets consumed, some work or effort to move and store data takes place and the by product is heat that needs to be removed. In a typical IT data center, cooling on average can account for about 50% of energy used with some sites using less.
With cooling being a large consumer of electricity, a small percentage change to how cooling consumes energy can yield large results. Addressing cooling energy consumption can be to discuss budget or cost issues, or to enable cooling capacity to be freed up to support installation of extra storage or other IT equipment.
Keep in mind that effective cooling relies on removing heat from as close to the source as possible to avoid over cooling which requires more energy. If you have not done so, have a facilities review or assessment performed that can range from a quick walk around, to a more in-depth review and thermal airflow analysis. A means of removing heat close to the sort are techniques such as intelligent, precision or smart cooling also known by other marketing names.
Powering Up, or, Powering Down
Speaking of energy or power, in addition to addressing cooling, there are a couple of ways of addressing power consumption by storage equipment (Figure 1). The most popular discussed approach towards efficiency is energy avoidance involving powering down storage when not used such as first generation MAID at the cost of performance.
For off-line storage, tape and other removable media give low-cost capacity per watt with low to no energy needed when not in use. Second generation (e.g. MAID 2.0) solutions with intelligent power management (IPM) capabilities have become more prevalent enabling performance or energy savings on a more granular or selective basis often as a standard feature in common storage systems.

Figure 1: How various RAID levels and configuration impact or benefit footprint constraints
Another approach to energy efficiency is seen in figure 1 which is doing more work for active applications per watt of energy to boost productivity. This can be done by using same amount of energy however doing more work, or, same amount of work with less energy.
For example instead of using larger capacity disks to improve capacity per watt metrics, active or performance sensitive storage should be looked at on an activity basis such as IOP, transactions, videos, emails or throughput per watt. Hence, a fast disk drive doing work can be more energy-efficient in terms of productivity than a higher capacity slower disk drive for active workloads, where for idle or inactive, the inverse should hold true.
On a go forward basis the trend already being seen with some servers and storage systems is to do both more work, while using less energy. Thus a larger gap between useful work (for active or non idle storage) and amount of energy consumed yields a better efficiency rating, or, take the inverse if that is your preference for smaller numbers.
Reducing Data Footprint Impact
Data footprint impact reduction tools or techniques for both on-line as well as off-line storage include archiving, data management, compression, deduplication, space-saving snapshots, thin provisioning along with different RAID levels among other approaches. From a storage access standpoint, you can also include bandwidth optimization, data replication optimization, protocol optimizers along with other network technologies including WAFS/WAAS/WADM to help improve efficiency of data movement or access.
Thin provisioning for capacity centric environments can be used to achieving a higher effective storage use level by essentially over booking storage similar to how airlines oversell seats on a flight. If you have good historical information and insight into how storage capacity is used and over allocated, thin provisioning enables improved effective storage use to occur for some applications.
However, with thin provisioning, avoid introducing performance bottlenecks by leveraging solutions that work closely with tools that providing historical trending information (capacity and performance).
For a technology that some have tried to declare as being dead to prop other new or emerging solutions, RAID remains relevant given its widespread deployment and transparent reliance in organizations of all size. RAID also plays a role in storage performance, availability, capacity and energy constraints as well as a relief tool.
The trick is to align the applicable RAID configuration to the task at hand meeting specific performance, availability, capacity or energy along with economic requirements. For some environments a one size fits all approach may be used while others may configure storage using different RAID levels along with number of drives in RAID sets to meet specific requirements.
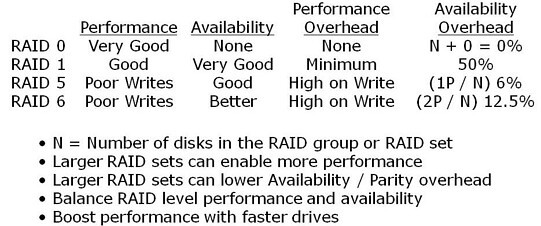
Figure 2: How various RAID levels and configuration impact or benefit footprint constraints
Figure 2 shows a summary and tradeoffs of various RAID levels. In addition to the RAID levels, how many disks can also have an impact on performance or capacity, such as, by creating a larger RAID 5 or RAID 6 group, the parity overhead can be spread out, however there is a tradeoff. Tradeoffs can be performance bottlenecks on writes or during drive rebuilds along with potential exposure to drive failures.
All of this comes back to a balancing act to align to your specific needs as some will go with a RAID 10 stripe and mirror to avoid risks, even going so far as to do triple mirroring along with replication. On the other hand, some will go with RAID 5 or RAID 6 to meet cost or availability requirements, or, some I have talked with even run RAID 0 for data and applications that need the raw speed, yet can be restored rapidly from some other medium.
Lets bring it all together with an example
Figure 3 shows a generic example of a before and after optimization for a mixed workload environment, granted you can increase or decrease the applicable capacity and performance to meet your specific needs. In figure 3, the storage configuration consists of one storage system setup for high performance (left) and another for high-capacity secondary (right), disk to disk backup and other near-line needs, again, you can scale the approach up or down to your specific need.
For the performance side (left), 192 x 146GB 15K RPM (28TB raw) disks provide good performance, however with low capacity use. This translates into a low capacity per watt value however with reasonable IOPs per watt and some performance hot spots.
On the capacity centric side (right), there are 192 x 1TB disks (192TB raw) with good space utilization, however some performance hot spots or bottlenecks, constrained growth not to mention low IOPS per watt with reasonable capacity per watt. In the before scenario, the joint energy use (both arrays) is about 15 kWh or 15,000 watts which translates to about $16,000 annual energy costs (cooling excluded) assuming energy cost of 12 cents per kWh.
Note, your specific performance, availability, capacity and energy mileage will vary based on particular vendor solution, configuration along with your application characteristics.

Figure 3: Baseline before and after storage optimization (raw hardware) example
Building on the example in figure 3, a combination of techniques along with technologies yields a net performance, capacity and perhaps feature functionality (depends on specific solution) increase. In addition, floor-space, power, cooling and associated footprints are also reduced. For example, the resulting solution shown (middle) comprises 4 x 250GB flash SSD devices, along with 32 x 450GB 15.5K RPM and 124 x 2TB 7200RPM enabling an 53TB (raw) capacity increase along with performance boost.
The previous example are based on raw or baseline capacity metrics meaning that further optimization techniques should yield improved benefits. These examples should also help to discuss the question or myth that it costs more to power storage than to buy it which the answer should be it depends.
If you can buy the above solution for say under $50,000 (cost to power), or, let alone, $100,000 (power and cool) for three years which would also be a good acquisition, then the myth of buying is more expensive than powering holds true. However, if a solution as described above costs more, than the story changes along with other variables include energy costs for your particular location re-enforcing the notion that your mileage will vary.
Another tip is that more is not always better.
That is, more disks, ports, processors, controllers or cache do not always equate into better performance. Performance is the sum of how those and other pieces working together in a demonstrable way, ideally your specific application workload compared to what is on a product data sheet.
Additional general tips include:
- Align the applicable tool, technique or technology to task at hand
- Look to optimize for both performance and capacity, active and idle storage
- Consolidated applications and servers need fast servers
- Fast servers need fast I/O and storage devices to avoid bottlenecks
- For active storage use an activity per watt metric such as IOP or transaction per watt
- For in-active or idle storage, a capacity per watt per footprint metric would apply
- Gain insight and control of how storage resources are used to meet service requirements
It should go without saying, however sometimes what is understood needs to be restated.
In the quest to become more efficient and optimized, avoid introducing performance, quality of service or availability issues by moving problems.
Likewise, look beyond storage space capacity also considering performance as applicable to become efficient.
Finally, it is all relative in that what might be applicable to one environment or application need may not apply to another.
Ok, nuff said.
Cheers gs
Greg Schulz – Author Cloud and Virtual Data Storage Networking (CRC Press), The Green and Virtual Data Center (CRC Press) and Resilient Storage Networks (Elsevier)
twitter @storageio
All Comments, (C) and (TM) belong to their owners/posters, Other content (C) Copyright 2006-2026 Server StorageIO and UnlimitedIO LLC All Rights Reserved