![]()
Amazon Web Services (AWS) recently added EBS Optimized support for enhanced bandwidth EC2 instances (read more here). This industry trends and perspective cloud conversation is the third (tying the posts together) in a three-part series companion to the AWS EBS optimized post found here. Part I is here (closer look at EBS) and part II is here (closer look at S3).
![]()
Cloud and object storage access example via Cloud and Virtual Data Storage Networking
AWS cloud storage gateway
In 2012 AWS released their Storage Gateway that you can use and try for free here using either an EC2 Amazon Machine Instance (AMI), or deployed locally on a hypervisor such as VMware vSphere/ESXi. About a year ago I did a storage gateway post (First, second and third impressions) when it was first released. I will do a new post soon following up with my later impressions and experiences of having used it recently. For now, my quick (fourth impressions can be found here in this AWS Marketplace review). In general, the gateway is an AWS alternative to using third product gateway, appliances of software tools for accessing AWS storage.
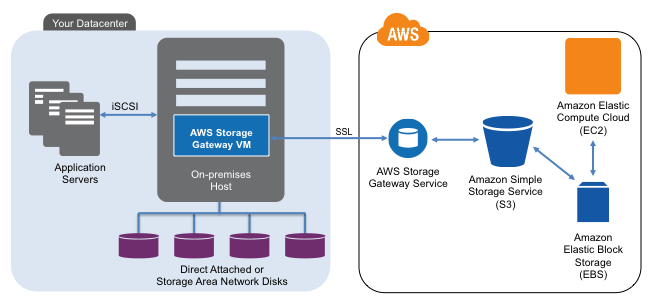
Image courtesy of www.amazon.com
When deployed locally on a VM, the storage gateway communicates using the AWS API’s back to the S3 and EBS (depending on how configured) storage services. Locally, the storage gateway presents an iSCSI block access method for Windows or other servers to use.
There are two modes with one being Gateway-Stored and the other Gateway-Cached. Gateway-Stored uses your primary storage mapped to the storage gateway as primary storage and asynchronous (time delayed) snapshots (user defined) to S3 via EBS volumes. This is a handy way to have local storage for low latency access, yet use AWS for HA, BC and DR, along with a means for doing migration into or out of AWS. Gateway-cache mode places primary storage in AWS S3 with a local cached copy to reduce network overhead.
![]()
When I tried the gateway a month or so ago, using both modes, I was not able to view any of my data using standard S3 tools. For example if I looked in my S3 buckets the objects do not appear, something that AWS said had to do with where and how those buckets and objects are managed. Otoh, I was able to see EBS snapshots for the gateway-stored mode including using that as a means of moving data between local and AWS EC2 instances. Note that regardless of the AWS storage gateway mode, some local cache storage is needed, and likewise some EBS volumes will be needed depending on what mode is used.
When I used the gateway, a Windows Server mounted the iSCSI volume presented by the storage gateway and in turn served that to other systems as a shared folder. Thus while having block such as iSCSI is nice, a NAS (NFS or CIFS) presentation and access mode would also be useful. However more on the storage gateway in a future post. Also note that beyond the free trial period (you may have to pay for storage being used) for using the gateway, there are also fees for S3 and EBS storage volumes use.
What about Glacier?
Shortly after its release last year, I did this piece about Glacier and have since been doing some testing proof of concepts with it.
I like Glacier and its prospects for doing some various things, particular for inactive data including deep archives that will seldom if every be accessed, yet need to be retained. The business value proposition of Glacier is that it has a very high durability and low-cost assuming that you do not need to frequently access your data, and when you do, that you can wait 3 to 5 hours before retrieving it from your S3 buckets.
Access to Glacier is via API or AWS console so getting things into and out of it can be a challenge. For example I wanted to see if I could use AWS storage gateway to more easily bulk move things into Glacier via S3, however no luck, or at least today. Speaking of S3, by setting your policies you determine when objects get moved into Glacier as well as how long they will stay there, you can read more about Glacier here and via AWS here.
![]()
How much do these AWS services cost?
Fees vary depending on which region is selected, amount of space capacity, level or durability and availability, performance along with type of service. S3 pricing can be found here including a free trial tier along with optional fees. Other AWS fees for EC2 can be found here, EBS pricing here, Glacier here, and storage gateway costs are located here.
Note that there is a myth that cloud vendors have hidden fees which may be the case for some, however so far I have not seen that to be the case with AWS. However, as a consumer, designer or architect, doing your homework and looking at the above links among others you can be ready and understand the various fees and options. Hence like procuring traditional hardware, software or services, do your due diligence and be an informed shopper.

Some more service cost notes include:
Note that with S3 Standard and RRS objects there is not a charge for deletion of objects, however there is a pro-rated charge per GByte of Glacier objects removed prior to 90 days. Glacier also allows up to 5% of your average monthly storage usage (pro-rated daily) to be restored with no charge, other fees apply for restoring larger amounts in a given period. Thus if you are planning on accessing and using data, analyze what your activity and usage will be as part of calculating your costs with Glacier. Read more about Glacier here.
Standard EBS volumes are changed by the amount of storage space capacity you provision in GB until released. For EBS snapshot copies there are fees for transferring data across regions, once moved, the rates of the new region apply for the snapshot.

As with Standard volumes, volume storage for Provisioned IOPS volumes is charged by the amount you provision in GB per month. With Provisioned IOPS volumes, you are also charged by the amount you provision in IOPS pro-rated as a percentage of days you have it in use for the month.
Thus important for cloud storage planning to know not only your space requirements, also IOP’s, bandwidth, and level of availability as well as durability. so for Standard volumes, you will likely see a lower number of I/O requests on your bill than is seen by your application unless you sync all of your I/Os to disk. Thus pay attention to what your needs are in terms of availability (accessibility), durability (resiliency or survivability), space capacity, and performance.
Leverage AWS CloudWatch tools and API’s to monitoring that matter for timely insight and situational awareness into how EBS, EC2, S3, Glacier, Storage Gateway and other services are being used (or costing you). Also visit the AWS service health status dashboard to gain insight into how things are running to help gain confidence with cloud services and solutions.
![]()
When it comes to Cloud, Virtualization, Data and Storage Networking along with AWS among other services, tools and technologies including object storage, we are just scratching the surface here.
Hopefully this helps to fill in some gaps giving more information addressing questions, along with generating new ones to prepare for your journey with clouds. After all, don’t be scared of clouds. Be prepared, do your homework, identify your concerns and then address those to gain cloud confidence.
Additional reading and related items:
Ok, nuff said (for now).
Cheers
Gs
Greg Schulz – Author Cloud and Virtual Data Storage Networking (CRC Press), The Green and Virtual Data Center (CRC Press) and Resilient Storage Networks (Elsevier)
twitter @storageio
All Comments, (C) and (TM) belong to their owners/posters, Other content (C) Copyright 2006-2026 Server StorageIO and UnlimitedIO LLC All Rights Reserved