Synopsis: EMC made a vision statement in a recent multimedia briefing that has a social networking angle as well as storage virtualization, virtual storage, public and private clouds.
Basically EMC provided a vision preview of in a social media networking friendly manner of a vision being refereed to initially as EMC Virtual Storage (aka twitter hash tag #emcvs) which of course sounds similar to a pharmacy chain.
The vision includes stirring up the industry with a new discussion around virtual storage compared to the decade old coverage of storage virtualization.
The underlying theme of this vision is similar to that of virtual serves vs. server virtualization including the ability to move servers around, so to should there be the ability to move data around more freely on a local or global basis and in real or near real time. In other words, breaking the decades long affinity that has existed between data storage and the data that exists on it (Figure 1). Buzzword bingo themes include federated storage, virtual storage, public and private cloud along with global cache coherency among others.

Figure 1: EMC Virtual Storage (EMCVS) Vision
The rest of the story
On Thursday March 11th 2010 Pat Gelsinger (EMC President and COO, Information Infrastructure Products) held an interactive briefing with the global analyst community pertaining to future EMC trajectory or visions. One of the interesting things about this session was that it was not unique to industry analysts nor was it under NDA.
For example, here is a link that if still active, should provide access to the briefing material.
The vision being talked about include those that EMC has talked about in the past such as virtualized data centers, or, putting a spin on the phrase data center virtualization, along with public and private clouds as well as infrastructure resource management virtualization (Figure 2):

Figure 2: Public and Private Clouds along with Virtual Data Centers
Figure 2 is a fairly common slide used in many EMC discussions positing public and private clouds along with virtualized data centers.

Figure 3: Tenants of the EMC Virtual Storage (EMCVS) vision

Figure 4: Enabling mobile data, breaking data and storage affinity

Figure 5: Enabling teleporting and virtual storage
Thus setting up the story for the need and benefit of distributed cache coherency, similar to distributed lock management (DLM) used on local and wide area clustered file systems for maintain data integrity.
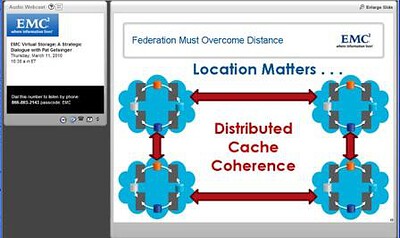
Figure 6: Leveraging distributed cache coherency
This discussion around distributed cache coherency should ring Dejavu of IBM GDPS (Global Dispersed Parallel Sysplex) for Mainframe, OpenVMS distributed lock management for VAX and Alpha clusters, Oracle RAC, or other parallel and clustered file systems among others. Likewise for those familiar with technology from Yotta Yotta, this should also ring familiar.
However while many are jumping on the Yotta Yotta familiarity bandwagon given comments made by Pat Gelsinger, something that came to mind is what about EMC GDDR? Do not worry if that is an acronym or product you are not up on as an EMC follower as it stands for EMC Geographically Dispersed Disaster (GDDR) solution that is an alternative to IBMs proprietary GDPS. Perhaps there is none, perhaps this is some, however what role if any including lessons learned will come from EMCs experience with GDDR not to mention other clustered file systems?

Figure 7: The EMC vision as presented
One of the interesting things about the vision announcement and perhaps part of floating it out for discussion was a comment made by Pat Gelsinger. That comment was about enabling the wild Wild West for IT, something that perhaps one generation might enjoy, however a notion another would soon forget. Im sure the EMC marke3ting team including their new chief marketing officer (CMO) Jeremy Burton can fine tune with time.
More on the social networking and non NDA angle
As is often the case with many other vendors, these types of customer, partner, analyst or media briefings (either online or in person) are under some form of NDA or embargo as they contain forward looking, yet to be announced products, solutions, technologies or other business initiatives. Note, these types of NDA discussions are not typically the same as those that portray or pretend to be NDA in order to sound more important a few days before an announcement that has already been leaked to get extra coverage or what are also known as media embargos.
After some amount of time, usually the information is formerly made public that was covered in advanced briefings, along with additional details. Sometimes material covered under NDA is done so in advanced such that third parties can prepare reports, deep dive analysis or assessment and other content that is made available at announcement or shortly there. The material is often prepared partners, vars, media, analysts, consultants, customers or others outside of the announcing company via different venues ranging from print, online columns, blogs, tweets videos and more.
Lately there has been some confusion in the broader IT as well as other industries as to where and how to classify bloggers, tweeters or other social media practionier. After all, is a blogger an analyst, journalist, free lance writer, advisor, vendor, consultant, customer, var, investor, hobbyist, competitor not to mention how does information get feed to them?
Likewise, NDAs and embargo have joined the list of fodder topics that some do not like for various reasons yet like to complain about for others. There is a time and place for real NDAs that cover and address material, discussions and other information that should not be shared. However all to often NDAs get watered down particularly on the press release games where a vendor or public relations firm (PR) will dangle an announcement briefing a couple of days or perhaps a week or two prior to an announcement under the guise that it not be disclosed prior to formal announcement.
Where these NDAs get tricky is that often they are honored by some and ignored by others, thus, those who honor the agreement get left behind by those who break the story. Personally I do not mind real NDA that are tied to real confidential material, discussion or other information that needs to be kept under wraps for various reasons. However the value or issues of NDA is whole different discussion, for now, lets get back to what EMC did not announce in their recent non-NDA briefing.




Different organizations are addressing social media in various ways, some ignoring it, others embracing it regardless of what it is. EMC is an example of a vendor who has embraced social networking and social media along with traditional means of developing and maintaining relations with the media (media or press relations), customers, partners, vars, consultants, investors (e.g. investor relations) as well as analysts (analyst relations).
For example, EMC works with analysts in traditional ways as they do with the media and other groups, however they also recognize that while some analysts (or media or investors or partners or customers or vars etc) blog and tweet (among other social networking mediums), not all do (as is also the case with media, customers, vars and so forth). Likewise EMC from a social media and networking perspective does not appear to define audiences based on the medium or tool that they use, rather, in a matrix or multi dimensional approach.
That is, an analyst with a blog is a blogger, a var or independent consultant with a blog is a blogger, or a media person including free lance writers, journalist, reporters or publisher with a blog is a blogger as are vars, advisors, partners and competitors with blogs also treated as bloggers.

Some of the 2009 EMC Bloggers Lounge Visitors
Thus at their EMCworld event, admission to the bloggers lounge is as simple and non exclusive as having a blog to join regardless of what your role or usage of a blog happens to be. On the other hand, information is communicated via different channels such as for traditional press via public relations folks, investors through investors relations, analysts via analyst relations, partners and customers through their venues and so forth.
When you think about it, makes sense as after all, EMC sells and attaches storage to mainframes, open systems Windows, UNIX, Linux as well as virtual servers that use different tools, protocols, languages and points of interest. Thus it should not be surprising that their approach to communicating with different audiences leverage various mediums for diverse messages at multiple points in time.
What does all of this social media discussion have to do with the March 11 EMC event?
In my opinion, this was an experiment of sorts of EMC to test the waters by floating a new vision to their traditional pre brief audience in advance of talking with media prior to an actual announcement.
That is, EMC did not announce a new product, technology, initiative, business alliance or customer event, rather a vision and trajectory or signaling what they may be doing in the future.
How this ties to social media and networking is that rather than being an event only for those media, bloggers, tweeters, customers, consultants, vars, free lancers, partners or others who agreed to do so under NDA, EMC used the venue as an advance sounding board of sorts.
That is, by sticking to broad vision vs. propriety and confidential or sensitive topics, the discussion has been put out in advance in the open to stimulate discussion in traditional reports, articles, columns or related venues not to mention in temporal real time via twitter not to mention via blogs and beyond.
Does this mean EMC will be moving away from NDAs anytime soon? I do not think so as there is still very much a need for advanced (and not a couple of weeks prior to announcement) types of discussion around sensitive information. For example with the trajectory or visionary discussion last week by EMC, the short presentation and discussion, limited slides prompt more questions than they address.
Perhaps what we are seeing is a new approach or technique of how organizations can use and bring social networking mediums into the mainstream business process as opposed to being perceived as niche or experimental mediums.
The reason I think it was an experiment is that EMC practices both traditional analyst/media relations along with emerging social media networking relations that includes practioners that span both audiences. For some the social media bloggers and tweeters are a different audience than traditional media, writers, consultants or analysts, that is, they are a separate and unique audience.
Thus, it is in my opinion and like human knees, elbows, feet, hands, ears as well as, well, you get the picture I think that there are many different views or thoughts not to mention interpretations of social media, social networking, blogging, analysts, consultants, advisors, media or press, customers, partners, and so on with diverse roles, functions and needs.
Where this comes back to the topic of last weeks discussion is that of storage virtualization vs. virtual storage. Rest assured in the time since the EMC briefing and certainly in the weeks or months to come, there will be penalty of knees, elbows, hands and other body parts flying and signaling what is a particular view or definition of storage virtualization vs. virtual storage.
Of course, some of these will be more entertaining than others ranging from well rehearsed, in some cases over the past decade or more to new and perhaps even revolutionary ones of what is and what is not storage virtualization vs. virtual storage, let alone cloud vs. cluster vs. grid vs. federated and beyond.
Additional Comments and thoughts
In general, I like the trajectory vision EMC is rolling out even if it causes confusion between what is virtual storage vs. storage virtualization, after all, we have been hearing about storage virtualization for over a decade now if not longer. Likewise, there has been plenty of talk about public clouds so it is refreshing to see more discussion and less cloud ware or cloud marketecture and how to actually leverage what you have to adopt private cloud practices.
I suspect that as the EMC competition starts to hear or piece together what they think this vision is or is not, we should also start to hear some interesting stories, spins, counter pitches, debates, twitter fights, blog slams and YouTube videos, all of which also happen to consume more storage.
I also like what EMC is doing with social media and networking as a means or medium for building and maintain relationships as well as for information exchange complimenting traditional means and mediums.
In other words, EMC is succeeding with social networking by not using it just as another megaphone to talk at or over people, rather, as a means to engage, to get to know, to challenge, to exchange regardless of if you are a so called independent blogger, twitter, analyst, medial, constant, customer, var, investor, partner among others.
If you are not already doing so, here are some EMC folks who actively participate in two way dialogues across different areas with @lendevanna helping to facilitate and leverage the masses of various people and subject matter experts including @chuckhollis @c_weil @cxi @davegraham @gminks @mike_fishman @stevetodd @storageanarchy @storagezilla @Stu and @vcto among many others.
Note that for you non twitter types, the previous are twitter handles (names or addresses) that can be accessed by putting https://twitter.com in place of the @ sign. For example @storageio = https://twitter.com/storageio
Additional Comments and thoughts:
Some comments and thoughts among others that I posted via twitter last week during the briefing event:

Here are some twitter comments that I posted last week during the event with hash tag #emcvs:
Is what was presented on the #emcvs #it #storage #virtualization call NDA material = Negative
Is what was presented on the #emcvs #it #storage #virtualization call a product announcement = NOpe
Is what was presented on the #emcvs #it #storage #virtualization call a statement of direction = Kind of
Is what was presented on the #emcvs #it #storage #virtualization call a hint of future functionality = probably
Is what was presented on the #emcvs #it #storage #virtualization call going to be shared with general public = R U reading this?
Is what was presented on the #emcvs #it #storage #virtualization call going to be discussed further = Yup
Is what was presented on the #emcvs #it #storage #virtualization call going to confuse the industry = Maybe
Is what was presented on the #emcvs #it #storage #virtualization call going to confuse customers = Depends on story teller
Is what was presented on the #emcvs #it #storage #virtualization call going to confuse competition = probably
Is what was presented on the #emcvs #it #storage #virtualization call going to provide fodder/fuel for bloggers = Yup
Anything else to add about #emcvs #it #storage #virtualization call today = Stay tuned, watch and listen for more!
Some additional questions and my perspectives on those include:
- What did EMC announce? Nothing, it was not an announcement; it was a statement of vision.
- Why did EMC hold a briefing without an NDA and yet nothing was announced? It is my opinion that EMC has a vision that they want to float an idea or direction, thus, sharing a vision to get discussions going without actually announcing a specific product or technology.
- Is this going to be a repackaged version of the Invista storage virtualization platform? I do not believe so.
- Is this going to be a repackaged version of the intellectual property (IP) assets that EMC picked up from the defunct startup called Yotta Yotta? Given some references to, along with what some of the themes and discussions center around, it is my guess that there is some Yotta Yotta IP along with other technologies that may be part of any future possible solution.
- Who or what is YottaYotta? They were a late dot com startup founded in 2000 that went through various incarnations and value propositions with some solutions that shipped. Some of the late era IP included distributed cache coherency and distance enablement of large scale federated storage on a global basis.
- Can the Yotta Yotta (or here) technology really scale? That remains to be seen, Yotta Yotta had some interesting demos, proof of concept, early adopters and big plans, however they also amounted to Nada Nada, perhaps EMC can make a Lotta Lotta out of it!
Other questions are still waiting for answers including among others:
- Will EMC Virtual Storage (aka emcvs) become a common cure for typical IT infrastructure ailments?
- Will this restart the debate around the golden rule of virtualization being whoever controls the virtualization controls the gold and thus vendors lock in?
- Will this be a members only vision where only certain partners can participate?
- What will other competitors respond with, technology, and marketecture, FUD or something else?
- What are the specific details of when, where and how the vision is implemented?
- What will all of this cost, will it work with existing products or is a forklift upgrade needed?
- Has EMC bitten off more than they can chew or deliver on or is Pat Gelsinger and his crew racing down a mountain and out in front of their skis, or, is this brilliance beyond what we mere mortals can yet comprehend?
- Can global data cache coherency really be deployed with data integrity on a global and large scale without negatively impacting performance?
- Can EMC make Lotta Lotta with this vision?
Here is what some of the EMC bloggers have had to say so far:
Chuck Hollis aka @chuckhollis had this to say
Stuart Miniman aka @stu had this to say
Summing it up for now
Lets see how the rest of the industry responds to this as the vision rolls out and perhaps sooner vs. later becomes technology that gets deployed and used.
Im skeptical until more details are understood, however I also like it and intrigued by it if it can actually jump from Yotta Yotta slide ware to Lotta Lotta deployments.
Cheers gs
Greg Schulz – Author Cloud and Virtual Data Storage Networking (CRC Press, 2011), The Green and Virtual Data Center (CRC Press, 2009), and Resilient Storage Networks (Elsevier, 2004)
twitter @storageio
All Comments, (C) and (TM) belong to their owners/posters, Other content (C) Copyright 2006-2012 StorageIO and UnlimitedIO All Rights Reserved
![]()
![]()
![]()