Part one of this two-part post provided a summary of today’s EMC (@EMCflash) announcement around XtremIO and renaming VFCache to XtremSF and associated software as XtremSW.

Synopsis of announcement
- Product rollout and selective availability of the new all flash SSD array XtremIO
- Rename server-side PCIe ssd flash cards from VFCache to XtremSF
- New XtremSF models including enhanced multi-level cell (eMLC) with larger capacities
- Rename VFCache caching software to XtremSW (enables cache mode vs. target mode)
Now lets take a closer look at what was announced along with what it means in terms of Industry Trends and Perspectives.
XtremIO has been in customer beta for some time and now those along with some other early customers are able to acquire the product. In addition, EMC is opening up XtremIO to more prospective customers (Directed Availability) who have requirements or needs that line up with the products target market capabilities.

What this means is that XtremIO is not being simply put out into the general product population for broad distribution. Instead, it is being put into a controlled release (Directed Availability) to help customers, partners and EMC sales decide where best to use it and thus risk revenue prevention in other areas. The criteria or target opportunity (at least initially) are little-data applications including OLTP, server virtualization (where aggregation can cause aggravation) along with virtual desktop or VDI. In other words, many of the traditional or legacy IOP focused SSD opportunities.
In addition to XtremIO EMC has renamed their VFCache PCIe flash SSD cards (Launched February 2012) to XtremSF along with new models with both SLC and MLC nand flash. Also as part of today’s announcement EMC is renaming the cache software for XtremSF (e.g. VFCache) to be known as XtremSW. Now if that did not prompt the question of if you can now buy XtremSF as a target mode only card without the cache software the answer is yes.
What is XtremIO?
It is a new all flash SSD storage array. XtremIO is a Cluster, grid or collection of nodes called bricks with linear performance scaling providing block based all flash SSD storage. Data services consists of data footprint reduction (DFR) including inline global (across all nodes or bricks) dedupe on 4Kbyte chunks along with thin provisioning. Global dedupe is done on ingest using a combination of flash buffered meta-data (tables, index or dictionary) of what has been seen before along with multi-threaded software to leverage multi-core processors. Using the global dedupe at ingest; only new unique data is saved based on 4 Kbyte chunks.
Performance per EMC scales from one single node to more second node or a fourth node. Note: architecturally more nodes can be added with EMC indicating added models will be available in the future.
In addition to DFR, other data services including writable snapshots, and auto-load balancing when new bricks are added. Note that in a normal running XtremIO, data is automatically spread across the nodes for both performance and resiliency. Data only needs to be moved or load-balanced in the background when new bricks are added. Instant copy snapshots are supported along with writable snapshots. Currently replication is done via external EMC products such as VPLEX or RecoverPoint with statement of directions (SOD) for future enhancements.
Additional attributes of XtremIO include:
- Each node or brick (X-Brick) has up to
16 (16 was Gen 1 hardware platform, it is now 25 SSD drives) - All bricks are involved in IO and storage processing
- Positioned by EMC as Software Defined (no proprietary hardware)
- Four x 8Gb Fibre Channel (8GFC) and four x 10Gb Ethernet (iSCSI) per brick
- Bricks communicate with each other via a separate interconnect network or fabric
- Bricks have redundant processors (think of as controllers) with multiple sockets and cores
- 4KB random read IOP’s scale from 250K (one brick), 500K (two bricks) and 1 Million (four bricks). For 4K random write IOPS, the numbers are 100K, 200K and 400K across one, two and four brick configurations with low latency and all data services running (EMC supplied numbers)
In addition to 4K being a commonly used or referred to IO size, it is also the same size as the new industry standard Advanced Format (AF). Today the standard storage block, page or sector size is 512 bytes however AF moves that to a larger 4,096 bytes (e.g. 4KB) to closer align with larger IO sizes. Note that many HDD’s and some SSD’s today support AF and provide 512 byte emulation modes for compatibility.
What is XtremSF?
VFCache is renamed XtremSF with new models using eMLC as companion to existing SLC PCIe cards and blade server mezzanine cards. EMC is emphasizing performance metrics that matter including IOPs that are relative to customer workloads such as 4K, 8K or larger with mix of reads and writes with low latency. In addition to IOPs with latency, size along with reads or writes for little data, EMC is also showing bandwidth or throughput numbers for big-data and big-bandwidth.
Model | Capacity | Read Transfer GB/sec | Write Transfer GB/sec | Random 4K Read (IOPS) | Random 4K Write (IOPS) | Random 4K Mixed ( IOPS) | Read latency (usec) | Write latency (usec) |
2200 (eMLC) | 2.2 TB | 2.47 | 1.1 | 343K | 105K | 206K | 87us | 30us |
700 (SLC) | 700 GB | 2.9 | 1.8 | 712K | 197K | 411K | 50us | 13us |
550 (eMLC) | 550 GB | 1.36 | 512 MB/s | 174K | 49K | 96K | 87us | 37us |
350 (SLC) | 350 GB | 2.9 | 756 MB/s | 715K | 95K | 267K | 50us | 13us |
Sampling of SLC and eMLC XtremSF PCIe SSD cards performance characteristics (via EMC) including latency measured in microseconds). Note performance differences due to some cards being based on SLC and others on eMLC.
Additional attributes, some new and some previously announced include:
- 8X PCIe bandwidth lanes for performance
- No IO impact to applications during garbage collection
- Supports multi-core processor workloads with parallel design
- Low CPU overhead by off-loading functions to PCIe card
- Half-height, half-length PCIe form factor
- Wear-leveling for nand flash program/erase (P/E) cycle duration
Other storage, server and systems vendors including Cisco, Dell, HP, IBM, NetApp and Oracle offer various PCIe nand flash SSD cards either as target, cache or mixed modes. Manufactures or suppliers of PCIe nand flash SSD cache and target cards include among others FusionIO, Intel, LSI,
Micron , OCZ and Virident (who is partnered with Seagate).
What is XtremSW?
Server side flash software (not to be confused with FAST) for using XtremSF as a tier 0 (server-side) ssd cache or target. In target mode the XtremSF functions as a high performance persistent local dedicated direct attached storage (DAS) device. Cache mode enables frequently accessed data to be kept close to the applications off-loading underlying storage systems to be more effectively used. The XtremSW complements back-end storage systems for data protection and persistence along with investment protection of those assets.

What this all means
SSD is in your future, question is where, when and with what.
Why not just use SSD (DRAM and or nand flash) everywhere?
Keep in mind that in the data center (traditional, virtual or cloud) everything is not the same. Thus the simple answer is that there is not enough of it available at a low enough price point (think closer to Hard Disk Drives (HDD) costs) to fit into customers budget. Sure SSDs provide better performance and productivity benefits, however while there is no such thing as a data or information recession, there are budget constraints.
Another reason why SSD cant simply be used everywhere are physical (and logical) constraints such as amount of memory a server can directly access, or current DDR3 DIMMs (this could change with DDR4 according to Micron) can only address and work with DRAM, PCIe bus physical slot space, operating and hypervisor addressing limits among others.
If SSD (DRAM and or nand flash) were priced were priced low enough (e.g. much closer to HDDs) and available SSD including both DRAM and nand flash (SLC, MLC, eMLC, TLC, etc) along with emerging Phase Change Memory (PCM) are at the convergence of traditional memory and data storage. While some storage (or server) professionals may not agree, storage is an extension of memory and thus part of the traditional server and storage memory hierarchy shown below.
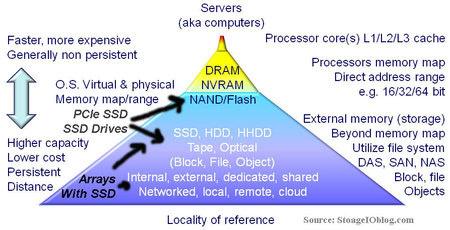
This brings up the locality of reference topic also shown in the following figure where the best IO is the one that does not have to be done. The second best is the one that can be done closest to application to a given level of service. Locality of reference which is important for servers and storage systems including caching refers to how close frequently accessed data is to where it is needed. For some applications this means as much DRAM main memory in a server as possible either clustered, with battery backup or other data persistency protection including onboard HDD or SSD (e.g. towards the top of the hierarchy).
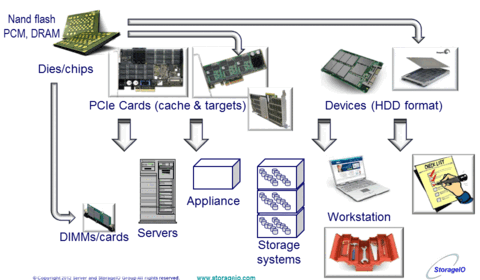
There are other applications where localized SSD (DRAM or nand flash) are a benefit to compliment main memory or as a persistent cache and target such as PCIe cards or SAS and SATA drives. Further down the stack and for housing larger amounts of storage with performance (reads or writes, random or sequential) along with data services is where all SSD and hybrid (mix of SSD and HDD) fit. Even further down the stack and for a broader segment is where cloud storage services based on SSD such as those from Rackspace (Cloud Block Storage with SSD) and Amazon (provisioned IOPS for EBS) have a play. Lets not forget about SSD in laptop, tablets and workstations, for example I have a Samsung model 830 in my Lenvo X1.

Some general industry trends include:
- SSD is like real estate, location can matter, a little can go a long way
- SSD media options include DRAM and nand flash (SLC, MLC, eMLC, TLC)
- Portfolios broadening with different products for various needs
- SSD functionality in servers, appliances, storage systems and cloud services
- All flash SSD arrays have not killed off all traditional or hybrid storage arrays
- Focus expanding from Just a Bunch Of SSD (JBOS) to enterprise like functionality
- Software needs hardware, hardware needs software, the two work better together
- Comparing meaningful metrics that matter vs. industry marketing metrics
Related items about nand flash, SSD and metrics related themes:

Some additional thoughts and perspectives
Does this mean traditional storage arrays are now dead?
IMHO, no, there will be some cannibalization of existing storage systems by XtremIO within EMC customers or prospects if not managed, as well as via those from others. Keep in mind that recently EMC announced enhancements to their VMAX including entry-level options for service providers. Some new opportunities opened up will be where traditional all SSD (flash or dram) systems have historically had success.
Traditional SSD and new dedicated SSD systems include Texas Memory Systems (TMS) bought by IBM in 2012, and the recently announced NetApp EF540 (and future FlashRay) along with startups Solidfire, Violin, Whiptail among others. There will be environments where XtremIO may take care of all storage needs for a customer or specific application or piece of it. Then there will be other situations where XtremIO will go-exist with EMC or other vendor’s storage solutions as part of a data infrastructure.

Who will EMC be competing against with XtremIO?
Certainly the startups or smaller players such as Violin, Whiptail, Purestorage, Solidfire along with IBM/TMS and NetApp EF540 (eventually FlashRay as well) among others.
There will also be some competition with other hybrid storage array vendors that have a mix of HDD and SSD. XtremIO will also compete in some situations on its own vs. other PCIe flash target and cache cards such as FusionIO, however for the most part those will up against XtremSF and XtremSW.
Why the slow or “Directed Availability” rollout?
Why not? By taking a controlled rollout selecting and qualifying customers for XtremIO, EMC gets to manage how the product goes out into production and control how it is used to increase chances of success. Unlike a startup that would be forced to try to put their new technology anywhere, EMC has the luxury of selecting where it goes, not to mention needing to avoid introducing a revenue prevention play for its other products.
Overall, I give an Atta boy and Atta girl to the EMC crew for a Product Defined Announcement (PDA) extending their flash portfolio to complement their different customers and prospects various environment needs. Now watch EMC, NetApp and others step up their flash dance moves to see who will out flash the others in the eXtreme flash games, not to mention emerging software defined marketing moves (SDMM) ;) .
Ok, nuff said.
Cheers Gs
Greg Schulz – Author Cloud and Virtual Data Storage Networking (CRC Press), The Green and Virtual Data Center (CRC Press) and Resilient Storage Networks (Elsevier)
twitter @storageio
All Comments, (C) and (TM) belong to their owners/posters, Other content (C) Copyright 2006-2026 Server StorageIO and UnlimitedIO LLC All Rights Reserved
![]()
![]()

